Java Advanced Features
Encryption and Decryption
The Java Cryptography API enables you to encrypt and decrypt data in Java, as well as manage keys, sign and authenticate messages, calculate cryptographic hashes and much more. The term cryptography is often abbreviated to crypto, so sometimes you will see references to Java crypto instead of Java Cryptography. The two terms refer to the same topic though.
The Java Mac class is used to create a MAC from a message. The term MAC is short for Message Authentication Code. A MAC is similar to a message digest, but uses an additional key to encrypt the message digest. Only by having both the original data and the key can you verify the MAC. Thus, a MAC is a more secure way to guard a block of data from modification than a message digest. The Mac class is described in more detail in the Java Mac tutorial, but below is a short introduction.
You create a Java Mac instance by calling the Mac.getInstance() method, passing as parameter the name of the algorithm to use. Here is how that looks:
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.security.spec.AlgorithmParameterSpec;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class EncryptionService {
private static final String cipher_type = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";// same as PKCS7 padding mode
private static int IV_SIZE = 16; // 128 bit
private final byte[] encryption_key;
private final byte[] auth_key;
/**
*
* @param encryption_key
* must be 44 bytes and Base64 encoded<br>
* @param auth_key
* must be 44 bytes and Base64 encoded<br>
*/
public EncryptionService(String encryption_key, String auth_key) throws Exception {
this.encryption_key = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryption_key);
this.auth_key = Base64.getDecoder().decode((auth_key));
}
public String encrypt(String inputStr) throws Exception {
byte[] input = inputStr.getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] iv = generateIV();
byte[] ciphertext = encrypt(encryption_key, iv, input);
byte[] ivcipher = concat(iv, ciphertext);
byte[] hmac = generateHMAC(auth_key, ivcipher);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(concat(ivcipher, hmac));
}
public String encryptAndUrlEncode(String input) throws Exception {
String encryptedInput = encrypt(input);
return URLEncoder.encode(encryptedInput, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.toString());
}
public String decrypt(String base64_payload) throws Exception {
byte[] encrypted_payload = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64_payload);
byte[] iv = Arrays.copyOf(encrypted_payload, IV_SIZE);
int macLenght = hmacLength(auth_key);
byte[] hmac1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(encrypted_payload, encrypted_payload.length - macLenght, encrypted_payload.length);
byte[] ciphertext = Arrays.copyOfRange(encrypted_payload, IV_SIZE, encrypted_payload.length - macLenght);
byte[] data = concat(iv, ciphertext);
byte[] hmac2 = generateHMAC(auth_key, data);
if (Arrays.equals(hmac1, hmac2)) {
byte[] decrypt = decrypt(encryption_key, iv, ciphertext);
return new String(decrypt, "UTF-8");
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Incorrect HMAC");
}
}
public String decryptUrlEncodedPayload(String urlEncodedPayload) throws Exception {
String decodedPayload = URLDecoder.decode(urlEncodedPayload, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.toString());
return this.decrypt(decodedPayload);
}
private byte[] generateIV() throws Exception {
byte[] iv = new byte[IV_SIZE];
SecureRandom randomSecureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");
randomSecureRandom.nextBytes(iv);
return iv;
}
private byte[] encrypt(byte[] skey, byte[] iv, byte[] data) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(skey, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(cipher_type);
AlgorithmParameterSpec param = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, param);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
private byte[] decrypt(byte[] skey, byte[] iv, byte[] data) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(skey, "AES");
AlgorithmParameterSpec param = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(cipher_type);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, param);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
/*
* Generate Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
*/
private byte[] generateHMAC(byte[] skey, byte[] data) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(skey, "HmacSHA256");
Mac sha256_HMAC = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
sha256_HMAC.init(key);
return sha256_HMAC.doFinal(data);
}
private int hmacLength(byte[] skey) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(skey, "HmacSHA256");
Mac sha256_HMAC = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
sha256_HMAC.init(key);
return sha256_HMAC.getMacLength();
}
private byte[] concat(byte[] first, byte[] second) {
byte[] result = Arrays.copyOf(first, first.length + second.length);
System.arraycopy(second, 0, result, first.length, second.length);
return result;
}
}
@Test
public void test_encryption() throws Exception {
// // must be 44 bytes or more
// String encryptionKey = "/I+CI2+sX6Z1aAr/6U6B1NuXjogJXbY0LATv6Ew1L6M=";
//
// // must be 44 bytes or more
// String authKey = "bpyp6QiIHE/h8Uh0OTvghrNd+x7ez+vEtX+GQ8tpwVk=";
String encryptionKey = new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode("testtesttesttesttesttesttesttest".getBytes()));
String authKey = new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode("testtesttesttesttesttesttesttest".getBytes()));
System.out.println(new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptionKey)));
System.out.println(new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(authKey)));
EncryptionService encryptionService = new EncryptionService(encryptionKey, authKey);
String inputStr = "hello";
System.out.println("inputStr: " + inputStr);
String encryptedStr = encryptionService.encrypt(inputStr);
System.out.println("encryptedStr: " + encryptedStr);
String decryptedStr = encryptionService.decrypt(encryptedStr);
System.out.println("decryptedStr: " + decryptedStr);
}
testtesttesttesttesttesttesttest testtesttesttesttesttesttesttest inputStr: hello encryptedStr: XdNGUYxx/eiTR4s2r1OSDuytHAd4vFAtbVZZUFESWM7QV4ftQpwVQEt22i77Xq6fFSCGEWDLyKps7KxKgB+7Qg== decryptedStr: hello
log4j
Logging is a very important part of software development. A well-written logging code offers quick debugging, easy maintenance, and structured storage of an application’s runtime information.
Logging does have its drawbacks also. It can slow down an application. If too verbose, it can cause scrolling blindness. To alleviate these concerns, log4j is designed to be reliable, fast and extensible.
Since logging is rarely the main focus of an application, the log4j API strives to be simple to understand and to use.
Log4j is fast, threadsafe, uses multiple levels, namely ALL, TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR and FATAL and more.
In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to use log4j in your application.
Include the log4j jar file in your classpath or include this dependency in your maven file
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
Create a log4j property file and put it into the root folder.
log4j.rootLogger=TRACE, consoleAppender, fileAppender
log4j.appender.consoleAppender=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.consoleAppender.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.consoleAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=[date: %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] [priority: %-5p] [thread: %t] [memberUuid: %X{memberUuid}] [class&line: %c{2}.%M:%L] [msg: %m]%n
# log to file
log4j.appender.fileAppender=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.fileAppender.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.fileAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=[date: %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] [priority: %-5p] [thread: %t] [memberUuid: %X{memberUuid}] [class&line: %c{2}.%M:%L] [msg: %m]%n
log4j.appender.fileAppender.File=application.log
But let’s break down the ConversionPattern layout. You can refer to its documentation here.
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} = Date and time format, refer to SimpleDateFormat JavaDoc.
%-5p = The logging priority, like DEBUG or ERROR. The -5 is optional, for the pretty print format.
%c{1} = The logging name we set via getLogger(), refer to log4j PatternLayout guide.
%M = Used to output the method name where the logging request was issued. WARNING Generating caller location information is extremely slow and should be avoided unless execution speed is not an issue.
%L = The line number from where the logging request.
%t = Used to output the name of the thread that generated the logging event.
%m%n = The message to log and line break.
%X = Used to output the MDC (mapped diagnostic context) associated with the thread that generated the logging event. The X conversion character must be followed by the key for the map placed between braces, as in %X{clientNumber} where clientNumber is the key. The value in the MDC corresponding to the key will be output.
For an application to have appropriate logs, you must have at least a console logs and a file containing logs. You can see the logs at real time while debugging and also you can go back to a previous log for a specific point in time.
You can even save your logs into a database
# Define the root logger with appender file
log4j.rootLogger = DEBUG, DB
# Define the DB appender
log4j.appender.DB=org.apache.log4j.jdbc.JDBCAppender
# Set JDBC URL
log4j.appender.DB.URL=jdbc:mysql://localhost/DBNAME
# Set Database Driver
log4j.appender.DB.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# Set database user name and password
log4j.appender.DB.user=user_name
log4j.appender.DB.password=password
# Set the SQL statement to be executed.
log4j.appender.DB.sql=INSERT INTO LOGS VALUES('%x','%d','%C','%p','%m')
# Define the layout for file appender
log4j.appender.DB.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
create a database table
CREATE TABLE LOGS
(USER_ID VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
DATED DATE NOT NULL,
LOGGER VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LEVEL VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
MESSAGE VARCHAR(1000) NOT NULL
);
Create a Logger field.
Logger log = Logger.getLogger(MainLog.class);
Log levels
Trace – Designates finer-grained informational events than the DEBUG.
Debug – Designates fine-grained informational events that are most useful to debug an application.
Info – Designates informational messages that highlight the progress of the application at coarse-grained level.
Warn – Designates potentially harmful situations.
Error – Designates error events that might still allow the application to continue running.
Fatal – Designates very severe error events that will presumably lead the application to abort.
All – All levels including custom levels.
Off – The highest possible rank and is intended to turn off logging.
import org.apache.log4j.PropertyConfigurator;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.log4j.PropertyConfigurator;
public class MainLog {
static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(MainLog.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
PropertyConfigurator.configure("log4j.properties");
log.trace("Trace Message Logged !!!");
log.debug("Debug Message Logged !!!");
log.info("Info Message Logged !!!");
log.error("Error Message Logged !!!");
log.fatal("Fatal Message Logged !!!");
}
}
[date: 2020-10-18 01:58:20] [priority: TRACE] [thread: main] [memberUuid: ] [class&line: lovemesomecoding.MainLog.main:16] [msg: Trace Message Logged !!!] [date: 2020-10-18 01:58:20] [priority: DEBUG] [thread: main] [memberUuid: ] [class&line: lovemesomecoding.MainLog.main:17] [msg: Debug Message Logged !!!] [date: 2020-10-18 01:58:20] [priority: INFO ] [thread: main] [memberUuid: ] [class&line: lovemesomecoding.MainLog.main:18] [msg: Info Message Logged !!!] [date: 2020-10-18 01:58:20] [priority: ERROR] [thread: main] [memberUuid: ] [class&line: lovemesomecoding.MainLog.main:19] [msg: Error Message Logged !!!] [date: 2020-10-18 01:58:20] [priority: FATAL] [thread: main] [memberUuid: ] [class&line: lovemesomecoding.MainLog.main:20] [msg: Fatal Message Logged !!!]
Database
Java uses the JDBC library to connect and manupilate databases. JDBC works with Java on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of UNIX.
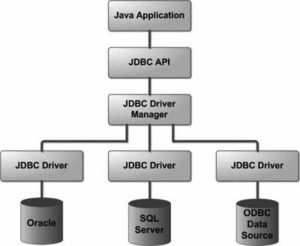
First, you need a connection. To create a connection, you need the username, password, and host for the database you want to connect to. Here I have a Enum to create a connection factory.
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public enum DBConnection {
INSTANCE("java_jdbc");
private Connection connection = null;
private String database;
private DBConnection(String database) {
this.database = database;
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/" + database + "?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String USER = "root";
String PASS = "";
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASS);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Connection getConnection() {
return connection;
}
public String getDatabase() {
return this.database;
}
}
Create a table
public static void createTable() {
System.out.println("creating " + TABLE_NAME + " table...");
DB_CONNECTION = DBConnection.INSTANCE.getConnection();
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = DB_CONNECTION.createStatement();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Check if table " + TABLE_NAME + " already exists.");
// @formatter:off
String checkTableSQL = "SELECT COUNT(*) as tableCount " +
"FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES " +
"WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '"+DBConnection.INSTANCE.getDatabase()+"' "+
"AND TABLE_NAME = '"+TABLE_NAME+"'; ";
// @formatter:on
try {
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + checkTableSQL);
ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(checkTableSQL);
resultSet.next();
int tableCount = resultSet.getInt("tableCount");
if (tableCount > 0) {
System.out.println("dropping " + TABLE_NAME + " table.");
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + "DROP TABLE " + TABLE_NAME + "; ");
boolean removedTable = stmt.execute("DROP TABLE " + TABLE_NAME + "; ");
System.out.println("table dropped " + removedTable);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("creating " + TABLE_NAME + " table.");
// @formatter:off
String createTableSQL = "CREATE TABLE "+TABLE_NAME+" " +
"(id INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, " +
" first_name VARCHAR(255), " +
" last_name VARCHAR(255), " +
" age INTEGER, " +
" PRIMARY KEY ( id )); ";
// @formatter:on
try {
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + createTableSQL);
stmt.executeUpdate(createTableSQL);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(TABLE_NAME + " table has been created!\n\n");
}
public static void insertDataToTable() {
System.out.println("inserting data into " + TABLE_NAME + " table...");
DB_CONNECTION = DBConnection.INSTANCE.getConnection();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
// load users
try {
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_USERS; i++) {
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
query.append("INSERT INTO user (first_name, last_name, age) ");
query.append("VALUES (?, ?, ?); ");
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + query.toString());
/**
* Use prepareStatement to insert data into the query and avoid SQL injection
*/
PreparedStatement pStmnt = DB_CONNECTION.prepareStatement(query.toString(), Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
String firstName = ConstantUtils.getRandomFirstname();
String lastName = ConstantUtils.getRandomLastname();
int age = RandomGeneratorUtils.getIntegerWithin(1, 51);
pStmnt.setString(1, firstName);
pStmnt.setString(2, lastName);
pStmnt.setInt(3, age);
System.out.println("parameter 1: " + firstName);
System.out.println("parameter 2: " + lastName);
System.out.println("parameter 3: " + age);
int numOfRowsCreated = pStmnt.executeUpdate();
if (numOfRowsCreated > 0) {
int id = 0;
ResultSet rs = pStmnt.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rs.next()) {
id = rs.getInt(1);
}
System.out.println("new id: " + id);
}
}
DB_CONNECTION.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
}
System.out.println(TABLE_NAME + " table has been populated with " + NUMBER_OF_USERS + " rows!\n\n");
}
public static void readDataFromTable(int selectedId) {
System.out.println("reading data from " + TABLE_NAME + " table...");
DB_CONNECTION = DBConnection.INSTANCE.getConnection();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement pStmnt = null;
// Read user
try {
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
query.append("SELECT id, first_name, last_name, age ");
query.append("FROM user ");
query.append("WHERE id = ? ");
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + query.toString());
pStmnt = DB_CONNECTION.prepareStatement(query.toString());
pStmnt.setInt(1, selectedId);
System.out.println("parameter 1: " + selectedId);
rs = pStmnt.executeQuery();
DB_CONNECTION.commit();
rs.next();
User user = User.generateUserFromResultset(rs);
System.out.println(user.toString());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (pStmnt != null) {
pStmnt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
System.out.println("Row with id=" + selectedId + " has been retrived from " + TABLE_NAME + ".\n\n");
}
public static void updateDataInTable(int selectedId) {
System.out.println("updating data in " + TABLE_NAME + " table...");
DB_CONNECTION = DBConnection.INSTANCE.getConnection();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Update user
try {
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
query.append("UPDATE user ");
query.append("SET first_name = ? ");
query.append(", age = ? ");
query.append("WHERE id = ? ");
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + query.toString());
PreparedStatement pStmnt = DB_CONNECTION.prepareStatement(query.toString());
int age = RandomGeneratorUtils.getIntegerWithin(1, 51);
String firstName = "Folau";
pStmnt.setString(1, firstName);
pStmnt.setInt(2, age);
pStmnt.setInt(3, selectedId);
System.out.println("parameter 1: " + firstName);
System.out.println("parameter 2: " + age);
System.out.println("parameter 3: " + selectedId);
pStmnt.executeUpdate();
DB_CONNECTION.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(TABLE_NAME + " table has been updated for row with id=" + selectedId + "!\n\n");
}
- Set autocommit to false
DB_CONNECTION.setAutoCommit(false);
- Commit changes when things are ok
DB_CONNECTION.commit();
- Roll back when things are not ok
DB_CONNECTION.rollback();
public static void updateDataInTable(int selectedId) {
System.out.println("updating data in " + TABLE_NAME + " table...");
DB_CONNECTION = DBConnection.INSTANCE.getConnection();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Update user
try {
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
query.append("UPDATE user ");
query.append("SET first_name = ? ");
query.append(", age = ? ");
query.append("WHERE id = ? ");
System.out.println("SQL QUERY: " + query.toString());
PreparedStatement pStmnt = DB_CONNECTION.prepareStatement(query.toString());
int age = RandomGeneratorUtils.getIntegerWithin(1, 51);
String firstName = "Folau";
pStmnt.setString(1, firstName);
pStmnt.setInt(2, age);
pStmnt.setInt(3, selectedId);
System.out.println("parameter 1: " + firstName);
System.out.println("parameter 2: " + age);
System.out.println("parameter 3: " + selectedId);
pStmnt.executeUpdate();
DB_CONNECTION.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException, msg=" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
try {
DB_CONNECTION.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(TABLE_NAME + " table has been updated for row with id=" + selectedId + "!\n\n");
}
Regex
Regex for social security number validation
United States Social Security numbers are nine-digit numbers in the format AAA-GG-SSSS with following rules.
- The first three digits called the area number. The area number cannot be 000, 666, or between 900 and 999.
- Digits four and five are called the group number and range from 01 to 99.
- The last four digits are serial numbers from 0001 to 9999.
Regex : ^(?!000|666)[0-8][0-9]{2}-(?!00)[0-9]{2}-(?!0000)[0-9]{4}$
^ # Assert position at the beginning of the string.
(?!000|666) # Assert that neither "000" nor "666" can be matched here.
[0-8] # Match a digit between 0 and 8.
[0-9]{2} # Match a digit, exactly two times.
- # Match a literal "-".
(?!00) # Assert that "00" cannot be matched here.
[0-9]{2} # Match a digit, exactly two times.
- # Match a literal "-".
(?!0000) # Assert that "0000" cannot be matched here.
[0-9]{4} # Match a digit, exactly four times.
$ # Assert position at the end of the string.
static String regex = "^(?!000|666)[0-8][0-9]{2}-(?!00)[0-9]{2}-(?!0000)[0-9]{4}$";
private static Pattern emailPattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
public static Boolean isValidSSNFormat(String ssn) {
if(ssn==null || ssn.length()==0) {
return false;
}
return emailPattern.matcher(ssn).matches();
}
Regex for email validation
public class EmailRegex {
static String regex = "^[a-zA-Z0-9_!#$%&’*+/=?`{|}~^.-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+$";
private static Pattern emailPattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
public static Boolean isValidEmailFormat(String email) {
if(email==null || email.length()==0) {
return false;
}
return emailPattern.matcher(email).matches();
}
}
public class EmailRegexDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String email = "folau@gmail.com";
boolean valid = EmailRegex.isValidEmailFormat(email);
System.out.println(email+" is a valid email = "+valid);
}
}
Regex for password validation
Password validation is the need for almost all the applications today. There are various ways to do validate passwords from writing everything manually to use third party available APIs.
static String regex = "((?=.*[a-z])(?=.*d)(?=.*[@#$%])(?=.*[A-Z]).{6,16})";
/*
* (?=.*[a-z]) : This matches the presence of at least one lowercase letter.
* (?=.*d) : This matches the presence of at least one digit i.e. 0-9.
* (?=.*[@#$%]) : This matches the presence of at least one special character.
* ((?=.*[A-Z]) : This matches the presence of at least one capital letter.
* {6,16} : This limits the length of password from minimum 6 letters to maximum 16 letters.
*/
public static Boolean isValidPasswordFormat(String password) {
if(password==null || password.length()==0) {
return false;
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(password).matches();
}
US zipcode regex validation
/*
* ^ # Assert position at the beginning of the string.
* [0-9]{5} # Match a digit, exactly five times.
* (?: # Group but don't capture:
* - # Match a literal "-".
* [0-9]{4} # Match a digit, exactly four times.
* ) # End the non-capturing group.
* ? # Make the group optional.
* $ # Assert position at the end of the string.
*/
static String US_ZIPCODE_REGEX = "^[0-9]{5}(?:-[0-9]{4})?$";
public static Boolean isValidUSZipcodeFormat(String zipcode) {
if(zipcode==null || zipcode.length()==0) {
return false;
}
return Pattern.compile(US_ZIPCODE_REGEX).matcher(zipcode).matches();
}
public class ZipcodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> zips = new ArrayList<String>();
//Valid ZIP codes
zips.add("12345");
zips.add("12345-6789");
//Invalid ZIP codes
zips.add("123456");
zips.add("1234");
zips.add("12345-678");
zips.add("12345-67890");
for (String zip : zips)
{
boolean valid = ZipcodeRegex.isValidUSZipcodeFormat(zip);
System.out.println(zip+" is a valid US zipcode? "+valid);
}
}
}
12345 is a valid US zipcode? true 12345-6789 is a valid US zipcode? true 123456 is a valid US zipcode? false 1234 is a valid US zipcode? false 12345-678 is a valid US zipcode? false 12345-67890 is a valid US zipcode? false
UK zipcode regex validation
static String UK_ZIPCODE_REGEX = "^[A-Z]{1,2}[0-9R][0-9A-Z]? [0-9][ABD-HJLNP-UW-Z]{2}$";
public static Boolean isValidUKZipcodeFormat(String zipcode) {
if(zipcode==null || zipcode.length()==0) {
return false;
}
return Pattern.compile(UK_ZIPCODE_REGEX).matcher(zipcode).matches();
}
Regex for number of lines
StringBuilder line = new StringBuilder();
line.append("Hey man");
line.append("\n");
line.append("I like Java");
line.append("\n");
boolean valid = StringRegex.isValidLines(line.toString(), 2);
System.out.println("does \n===\n" + line.toString() + "===\nhas 2 lines? " + valid);
Regex for number of words
public static Boolean isValidLength(String str, int length) {
String regex = "^\\W*(?:\\w+\\b\\W*){1,"+length+"}$";
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(str).matches();
}
public class StringRegexDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> inputs = new ArrayList<String>();
inputs.add("Folaulau");
inputs.add("JAVA is great");
inputs.add("I love java programming");
inputs.forEach((input) -> {
int length = 10;
boolean valid = StringRegex.isValidLength(input, length);
System.out.println("is " + input + " " + length + " in length? " + valid);
});
}
}
# output
is Folaulau 10 in length? true
is JAVA is great 10 in length? true
is I love java programming 10 in length? true
Regex for ISBN
ISBN-10 or ISBN-13 : ^(?:ISBN(?:-1[03])?:? )?(?=[0-9X]{10}$|(?=(?:[0-9]+[- ]){3})
[- 0-9X]{13}$|97[89][0-9]{10}$|(?=(?:[0-9]+[- ]){4})[- 0-9]{17}$)
(?:97[89][- ]?)?[0-9]{1,5}[- ]?[0-9]+[- ]?[0-9]+[- ]?[0-9X]$
public class RegexISNBDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> isbns = new ArrayList<String>();
//Valid ISBNs
isbns.add("0-596-52068-9");
isbns.add("0 512 52068 9");
isbns.add("ISBN-10 0-596-52068-9");
isbns.add("ISBN-10: 0-596-52068-9");
//Invalid ISBNs
isbns.add("0-5961-52068-9");
isbns.add("11 5122 52068 9");
isbns.add("ISBN-13 0-596-52068-9");
isbns.add("ISBN-10- 0-596-52068-9");
isbns.forEach((isbn)->{
boolean valid = RegexISNB.isValidISBNFormat(isbn);
System.out.println("is "+isbn+" a valid ISBN? "+valid);
});
}
}
is 0-596-52068-9 a valid ISBN? true is 0 512 52068 9 a valid ISBN? true is ISBN-10 0-596-52068-9 a valid ISBN? true is ISBN-10: 0-596-52068-9 a valid ISBN? true is 0-5961-52068-9 a valid ISBN? false is 11 5122 52068 9 a valid ISBN? false is ISBN-13 0-596-52068-9 a valid ISBN? true is ISBN-10- 0-596-52068-9 a valid ISBN? false
Remove special characters from file name
/*
* Only alphabets[a-z] and digits[0-9], dot, underscore, dash
*/
String alphaAndDigits = "[^a-zA-Z0-9.-_]+";
String newFileName = fileName.replaceAll(alphaAndDigits, "");
@Test
public void test_replace_invalid_characters() {
String fileName = "test .jpg";
String newFileName = FileUtils.replaceInvalidCharacters(fileName);
System.out.println("newFileName=" + newFileName);
fileName = "test]&.jpg";
newFileName = FileUtils.replaceInvalidCharacters(fileName);
System.out.println("newFileName=" + newFileName);
fileName = "test$.jpg";
newFileName = FileUtils.replaceInvalidCharacters(fileName);
System.out.println("newFileName=" + newFileName);
fileName = "test@=`.jpg";
newFileName = FileUtils.replaceInvalidCharacters(fileName);
System.out.println("newFileName=" + newFileName);
}
newFileName=test.jpg newFileName=test.jpg newFileName=test.jpg newFileName=test.jpg
Generics