HTML Table of Content
HTML Doctypes
A DOCTYPE is an instruction to the web browser about the version of HTML in which the web page is written. A DOCTYPE declaration appears at the top of a web page before all other elements. According to the HTML specification or standards, every HTML document requires a valid document type declaration to insure that your web pages are displayed the way they are intended to be displayed.
The DOCTYPE for HTML5
<!DOCTYPE html>
Doctypes for earlier versions of HTML were longer because the HTML language was SGML-based and therefore required a reference to a DTD, but they are obsolete now.
With HTML5 this is no longer the case and the doctype declaration is only needed to enable the standard mode for documents written using the HTML syntax.
HTML4
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
You can use the following markup as a template to create a new HTML5 document.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
</body>
</html>
HTML Head Section
The <head> element contains metadata or information about the HTML page. It is a container for the following elements: <title>, <style>, <meta>, <link>, <script>, <noscript>, and <base>.
Title tag
The <title> tag defines the title of the document. The title must be text-only, and it is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab. The <title> tag is required in HTML documents!
The contents of a page title is very important for search engine optimization (SEO)! The page title is used by search engine algorithms to decide the order when listing pages in search results.
The <title> element:
- defines a title in the browser toolbar
- provides a title for the page when it is added to favorites
- displays a title for the page in search-engine results
Here are some tips for creating good titles:
- Go for a longer, descriptive title (avoid one- or two-word titles)
- Search engines will display about 50-60 characters of the title, so try not to have titles longer than that
- Do not use just a list of words as the title (this may reduce the page’s position in search results)
So, try to make the title as accurate and meaningful as possible!
Note: You can NOT have more than one <title> element in an HTML document.
<title>lovemesomecoding</title>
Style tag
The <style> tag is used to define style information (CSS) for a document. Inside the <style> element you specify how HTML elements should render in a browser. Note that when a browser reads a style sheet, it will format the HTML document according to the information in the style sheet. If some properties have been defined for the same selector (element) in different style sheets, the value from the last read style sheet will be used (see example below)!
<style>
p {color:black;}
</style>
Meta tag
The <meta> tag defines metadata about an HTML document. Metadata is data or information about data in your web page. <meta> tags are typically used to specify character set, page description, keywords, author of the document, and viewport settings.
Metadata is used by browsers (how to display content or reload page), search engines (keywords), and other web services. There is a method to let web designers take control over the viewport (the user’s visible area of a web page), through the <meta> tag. name specifies the type of meta element it is; what type of information it contains. content specifies the actual meta content.
<!-- charset --> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <!-- application-name, author, description, generator, keywords, viewport --> <meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript"> <meta name="application-name" content="lovemesomecoding"> <meta name="description" content="Free Web tutorials"> <meta name="author" content="John Doe"> <meta name="generator" content="folau"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <!-- http-equiv="content-security-policy|content-type|default-style|refresh" --> <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="30">
Link tag
The <link> tag defines the relationship between the current document and an external resource. The <link> tag is most often used to link to external style sheets. The <link> element is an empty element, it contains attributes only.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
Script tag
The <script> tag is used to embed a client-side script (JavaScript). The <script> element either contains scripting statements, or it points to an external script file through the src attribute.
Common uses for JavaScript are image manipulation, form validation, and dynamic changes of content.
Note: There are several ways an external script can be executed:
- If async=”async”: The script is executed asynchronously with the rest of the page (the script will be executed while the page continues the parsing)
- If async is not present and defer=”defer”: The script is executed when the page has finished parsing
- If neither async or defer is present: The script is fetched and executed immediately, before the browser continues parsing the page
<script type="text/javascript"> var username = 'folau'; </script>
NoScript tag
The <noscript> tag defines an alternate content to be displayed to users that have disabled scripts in their browser or have a browser that doesn’t support script. The <noscript> element can be used in both <head> and <body>. When used inside <head>, the <noscript> element could only contain <link>, <style>, and <meta> elements.
<noscript>Your browser does not support JavaScript!</noscript>
Base tag
The <base> tag specifies the base URL and/or target for all relative URLs in a document. The <base> tag must have either an href or a target attribute present, or both. There can only be one single <base> element in a document, and it must be inside the <head> element.
<base href="https://lovemesomecoding.com/" target="_blank">
HTML DOM
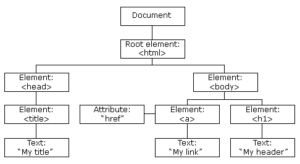
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for HTML. It defines:
- The HTML elements as objects
- The properties of all HTML elements
- The methods to access all HTML elements
- The events for all HTML elements
In other words:The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.
HTML Table
A table is a structured set of data made up of rows and columns. A table allows you to quickly and easily look up values that indicate some kind of connection between different types of data, for example a person and their age.
The <table> tag defines an HTML table. Each table row is defined with a <tr> tag. Each table header is defined with a <th> tag. Each table data/cell is defined with a <td> tag.
By default, the text in <th> elements are bold and centered.
By default, the text in <td> elements are regular and left-aligned.
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<th>Firstname</th>
<th>Lastname</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Folau</td>
<td>Kaveinga</td>
<td>33</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Lisa</td>
<td>Kaveinga</td>
<td>33</td>
</tr>
</table>
Colspan
To make a cell span more than one column, use the colspan attribute.
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th colspan="2">Telephone</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Folau</td>
<td>3101212123</td>
<td>3101212124</td>
</tr>
</table>
Rowspan
To make a cell span more than one row, use the rowspan attribute.
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<td>Folau</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th rowspan="2">Telephone</th>
<td>3101212123</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3101212124</td>
</tr>
</table>
Table with css
borderdefine a borderborder-collapsecollapse cell borderspaddingadd padding to cellstext-alignalign cell textborder-spacingset the spacing between cells
<style>
table {
border-spacing: 5px;
}
table, th, td {
border: 2px solid black;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
padding: 15px;
}
th {
text-align: left;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #eee;
}
tr:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: #fff;
}
</style>
HTML Graphics
Canvas
<canvas> is used to draw graphics, on the fly, via JavaScript. The <canvas> element is only a container for graphics. You must use JavaScript to actually draw the graphics.
Canvas has several methods for drawing paths, boxes, circles, text, and adding images.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-3">
<h3>Canvas</h3>
</div>
<div class="col-9">
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
Your browser does not support the HTML canvas tag.</canvas>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-3">
<h3>Canvas</h3>
</div>
<div class="col-9">
<canvas id="wordCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
Your browser does not support the HTML canvas tag.</canvas>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var c = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx = c.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(95, 50, 40, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.stroke();
var word = document.getElementById("wordCanvas");
var wCtx = word.getContext("2d");
wCtx.font = "30px Arial";
wCtx.fillText("Hello World",10,50);
</script>
SVG
The HTML <svg> element is a container for SVG graphics.
SVG has several methods for drawing paths, boxes, circles, text, and graphic images.
<svg width="100" height="100">
<circle cx="50" cy="50" r="40" stroke="green" stroke-width="4" fill="yellow" />
</svg>
CANVAS
|
SVG
|