Web Layer
1. MVC is an abbreviation for a design pattern. What does it stand for and what is the idea behind it?
Model–View–Controller software architectural pattern is designed to decouple three components, each of them can be easily swapped with a different implementation, and together they provide a fully functional user interface.
- Model: holds the current data and business logic.
- View: presenting data. User interacts with view.
- Controller: accept requests from view, issues commands to model; manipulate data from model, interacts with view.
Advantages:
- separation of concerns
- decoupling among MVC
- reuse of model and controllers with different views
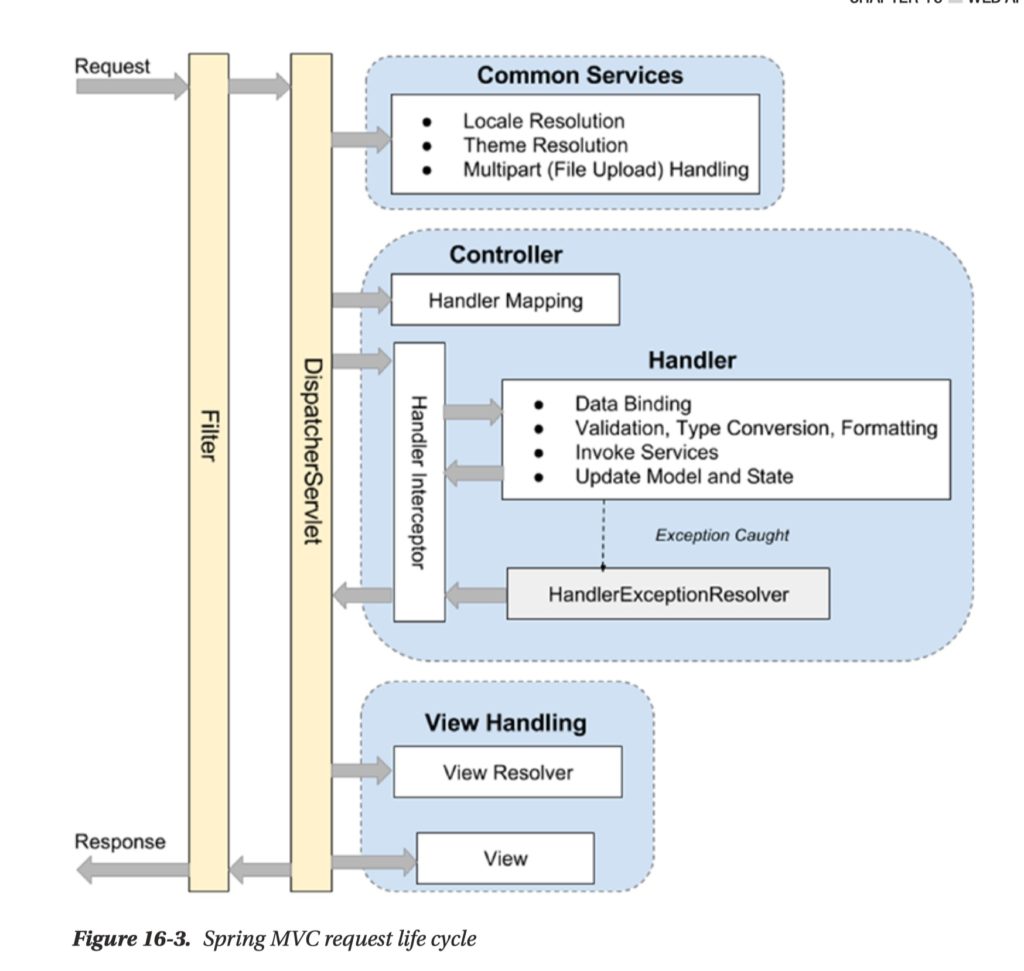
- Filter: The filter applies to every request. There are several commonly used filters.
- Dispatcher servlet: The servlet analyzes the requests and dispatches them to the appropriate controller for processing. This is where DispatcherServlet implement Front Controller design pattern.
- Common services: The common services will apply to every request to provide supports including i18n, theme, and file upload. Their configuration is defined in the DispatcherServlet’s WebApplicationContext.
- Handler mapping: This maps incoming requests to handlers (a method within a Spring MVC controller class). Spring MVC will automatically register a HandlerMapping implementation maps handlers based on HTTP paths expressed through the
@RequestMapping annotation at the type or method level within controller classes. - Handler interceptor: In Spring MVC, you can register interceptors for the handlers for implementing common checking or logic. For example, a handler interceptor can check to ensure that only the handlers can be invoked during office hours.
- Handler exception resolver: to deal with unexpected exceptions thrown during request processing by handlers.
- View Resolver: Spring MVC’s ViewResolver interface supports view resolution based on a logical name returned by the controller.
2. Do you need spring-mvc.jar in your classpath or is it part of spring-core?
- Yes, you do need this jar.
- It’s not part of Spring Core.
- It inclues Spring Core.
3. What is the DispatcherServlet and what is it used for?
DispatcherServlet is a front controller that receives all requests and delegates them to all the required controllers. But it is involved in more steps than just the first one. Among these are:
- receiving the initial request and handling it to the required controller
- checking for the required controller using handler mappings
- receiving the model and the view name from the controller and handling that to the required view after checking for that view with the view resolver (there are various types of resolvers for different view technologies – JSP, ThymeLeaf etc.)
- calling the view resolver
This servlet initializes a WebApplicationContext that is a child of root ApplicationContext.
Front controller pattern stands for a single servlet delegates responsibility for a request to other components of an application, to perform actual processing.Following front controller pattern, Spring MVC provides DispatcherServlet receiving all the requests and delegates the processing to request handlers (controllers). Once the processing is done, ViewResolver will render a view based on the view name.
A Spring web application may define multiple dispatcher servlets, each of which has its own namespace, its own Spring application context and its own set of mappings and handlers.
Used for- Recerives requests and delegates them to registered handlers
- Resolve views by mapping view-names to view instances
- Resolves exceptions
- Configuring the root
WebApplicationContext - Configuring the servlet filters required by Spring MVC
- Configuring the dispatcher servlets within the application
public class DemoWebAppInitializer
extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" }; // Map DispatcherServlet to /
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] { SecurityConfig.class, DataServiceConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { // Specify configuration class
return new Class<?>[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Filter getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter cef = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
cef.setEncoding("UTF-8");
cef.setForceEncoding(true);
return new Filter{ new HiddenHttpMethodFilter(), cef};
}
}
To make things more practical, Spring class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer, an implementation of WebApplicationInitializer, was extended because it contains concrete implementations of methods needed for the configuration of Spring web applications that use Java-based Spring configuration.
getRootConfigClasses(): A root application context of typeAnnotationConfigWebApplicationContextwill be created.getServletConfigClasses(): A web application context of type AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext will be createdgetServletMappings(): The DispatcherServelt’s mappings (context) are specified by the array of strings returned by this method.getServletFilters(): As the name of the methods says, this one will return an array of implementations of javax.servlet.Filter that will be applied to every request
By providing an empty class that extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer, you are basically telling Spring that you want DelegatingFilterProxy enabled, so springSecurityFilterChain will be used before any other registered javax.servlet.Filter.
- Any class that extends
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializerwill automatically be used to configureDispatcherServletand the Spring application context in the application’s servlet context. - This initializer create a
DispatcherServletand aContextLoaderListener. getServletMappings()identifies one or more paths that DispatcherServlet will be mapped to. It will handle all requests coming into the application.getRootConfigClasses()is called internally, and the configuration classes are used to create the root application context, which will become the parent ApplicationContext that contains bean definitions shared by all child (DispatcherServlet) contexts.
- /static
- /public
- /resources
- /META-INF/resources
4. Is the DispatcherServlet instantiated via an application context?
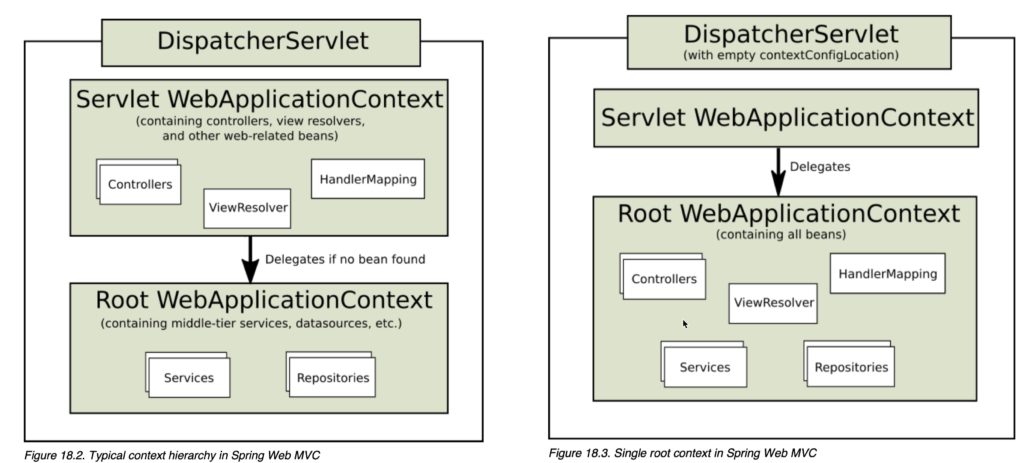
DispatcherServlet can be instantiated in 2 different ways and in both it is initialized by the servlet container:- Defining it in XML, specifically in the web.xml of the project.
- Using Java – since Servlet 3.0 you can use the ServletContext.addServlet() method for registering the DispatcherServlet in ServletContext. This is Done in more ways; the one I like is extending AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer which allows you to specify the web configuration class and the root application class at one time.
In short: the DispatcherServlet is not instantiated via an application context. It is instantiated before any application context is created. parent ApplicationContext is creted by ContextLoaderListener, child ApplicationContext is created by Spring MVC DispatcherServlet.
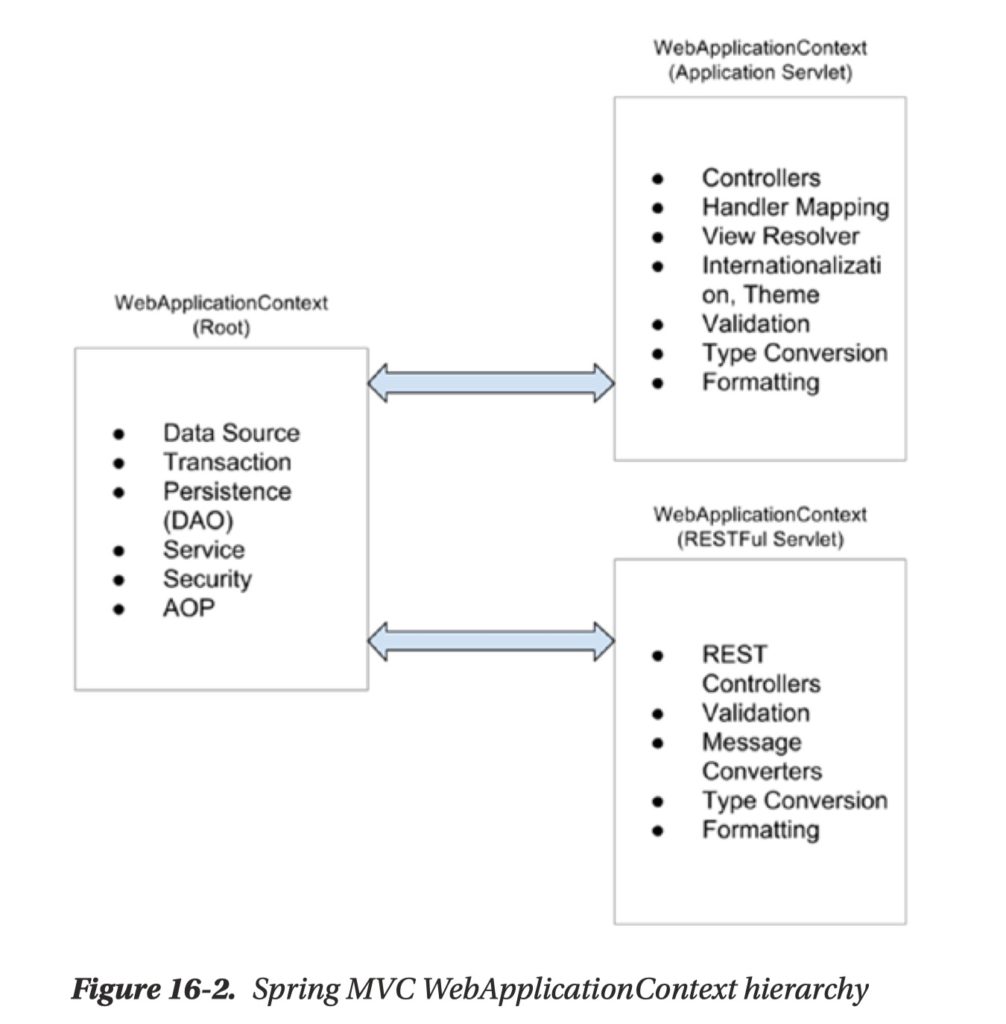
Parent ApplicationContext
- It is also called RootApplicationContext.
- In a web application, parent ApplicationContext is usually created using
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener. - it includes the application-level configurations such as the back-end data source, security, and service and persistence layer configuration.
- Say, it contains all non-web beans.
- It’s available to all servlet-level WebApplicationContexts.
- It is also called the web context or the DispatcherServletContext.
- It is created by Spring MVC
DispatcherServlet. - Beans in the web context can access the beans in the parent context, but not conversely.
- One servlet supports the user interface (called the application servlet), and
- the other provides services in the form of RESTful-WS to other applications (called the RESTful servlet).
DispatcherServlet can be instantiated in 2 different ways and in both it is initialized by the servlet container:
- XML
- Java bean
5. What is a web application context? What extra scopes does it offer?
WebApplicationContext is a Spring application context for web applications.Comparing to ApplicationContext
- WebApplicationContext has all the properties of a regular Spring application contex, given that the
WebApplicationContextinterface extends theApplicationContextinterface - WebApplicationContext can access the Servlet Context.
- You can always look up the WebApplicationContext using static methods from ServletContext.
- request: each http request
- session: each http session
- application: per
ServletContext
WebApplicationContext can also access the Servlet Context by implementing the ServletContextAware interface
public interface ServletContextAware extends Aware {
void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext);
}
6. What is the @Controller annotation used for?
@Controller annotation is used to mark a class as a controller to be used by the DispatcherServlet to process requests. @Controller annotation is annotated by @Component so in case your DispatcherServlet creates a WebApplicationContext that is configured by component-scanning, that configuration will pick @Controller annotated classes automatically.
You can define controllers without component-scanning and in that case, you will have to implement the Controller interface and override handleRequest() method.
The core interface in Spring MVC is Controller. Spring simply requires that- you implement the Controller interface
- or annotate your controller class with the @Controller annotation
The @EnableWebMvc annotation enables the annotation support for Spring MVC, that is, the @Controller annotation.
7. How is an incoming request mapped to a controller and mapped to a method?
When a request is issued to the application:
- DispatcherServlet of the application receives the request.
- DispatcherServlet maps the request to a method in a controller.
- DispatcherServlet holds a list of classes implementing the
HandlerMappinginterface. - DispatcherServlet dispatches the request to the controller.
- The method in the controller is executed.
8. What is the difference between @RequestMapping and @GetMapping?
@GetMapping equals to ` @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)`
9. What is @RequestParam used for?
The request parameter can be retrieved through a method argument annotated with@RequestParam
You can use the @RequestParam annotation to bind Servlet request parameters.
By default, method parameters that use this annotation are required, but you can specify that a method parameter is optional by
- setting the
@RequestParamannotation’s required flag tofalseor - by declaring the argument with an
java.util.Optionalwrapper.
NB. use of @RequestParam is optional. By default, any argument that is a simple value type (as determined by BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty) and is not resolved by any other argument resolver, is treated as if it were annotated with @RequestParam.
10. What are the differences between @RequestParam and @PathVariable?
@PathVariable instructs Spring MVC to bind the path variable within the URL – for example, http:// localhost:8080/singer/1 into the id argument of the findSingerById() method. – Note that for the id argument, the type is Long, while Spring’s type conversion system will automatically handle the conversion from String to Long for us.
@RequestMapping(value = "/{userId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String show(@PathVariable("userId") Long id, Model model) {
// ...
}
Differences:
http://localhost:8080/greeting?firstName=dammy&lastName=goodhttp://localhost:8080/firstname/dammy/lastname/good
11. What are some of the parameter types for a controller method?
- WebRequest
- ServletRequest
- ServletResponse
- HttpSession
- Principle
- HttpMethod
- Locale
- TimeZone
- java.io
- HttpEntity
- Collections, like Map<>
- Errors
- BindingResult
- SessionStatus
- UriComponentsbuilder
12. What other annotations might you use on a controller method parameter? (You can ignore form-handling annotations for this exam)
- @PathVariable
- @MatrixVariable: key-value pair in url
- @RequestParam
- @CookieValue
- @RequestBody
- @RequestHeader
- @RequestPart: “multipart/form-data”
- @ModelAttribute
- @SessionAttribute
- @SessionAttributes
- @RequestAttribute
13. What are some of the valid return types of a controller method?
- HttpEntity
- ResponseEntity
- HttpHeaders
- String
- View
- Map<>
- ModelAndView
- void
- CompletableFuture | CompletionStage: Asynchronous
14. What is a View and what’s the idea behind supporting different types of View?
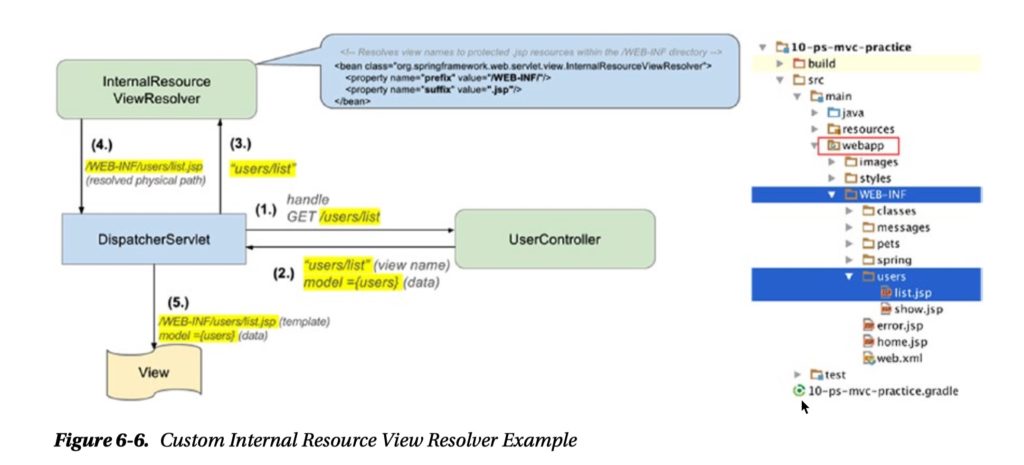
View is responsible for presenting the data of the application to the user.
The user interacts with the view. The core view resolver provided by Spring is theInternalResourceViewResolver; it is the default view resolver.
Inside spring-webmvc.jar there is a file called DispatcherServlet.properties, and in it all default infrastructure beans are declared.
Spring MVC provides several view resolvers to support multiple view technologies, such as JSP, Velocity, FreeMarker, JSF, Tiles, Thymeleaf, and so on.
supporting different types of views:
- Present model in different formats
- Adapt view to different platforms
- Use different view-technology
15. How is the right View chosen when it comes to the rendering phase?
View Resolution Sequence- Controller returns logical view name to
DispatcherServlet ViewResolversare asked in sequence (based on their Order)- If ViewResolver matches the logical view name then returns which View should be used to render the output. If not, it returns null and the chain continues to the next ViewResolver
- Dispatcher Servlet passes the model to the Resolved View and it renders the output
- If the view-name cannot be resolved, then an exception.
16. What is the Model?
- An instance of an object that implements the Model interface from the Spring framework
- It is a collection of key-value pairs.
- The contents of the model represents the state of the application and contains information that will be used when rendering the view.
- The value-objects contained in the model may also contain business logic implemented in the classes instantiated to create those objects.
17. Why do you have access to the model in your View? Where does it come from?
- It contains information that will be used when rendering the view.
- The model is passed as a parameter to the view when the dispatcher servlet asks the selected view to render itself as part of processing a request.
18. What is the purpose of the session scope?
A session-scoped Spring bean exists for the lifetime of a HTTP session. This enables creating, for instance, a session-scoped Spring bean that contains a shopping cart. The bean instance will remain the same during all requests the user makes within one and the same HTTP session.19. What is the default scope in the web context?
Singleton Scope is default scope.20. Why are controllers testable artifacts?
The goal of Spring MVC Test is to provide an effective way to test controllers by performing requests and generating responses through the actual DispatcherServlet.
The Spring MVC Test Framework also provide full Spring MVC runtime behavior for tests without running in a servlet container.
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(HomeController.class)
public class HomeControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;// Injects MockMvc
@Test public void testHomePage() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("home"))
.andExpect(content().string( containsString("Welcome to...")));
}
}
21. What does a ViewResolver do?
- A
ViewResolver, that is a class implementing the ViewResolver interface, attempts to, given a view name and a locale, find a View. - A
ViewResolverattempts to map a view name to a View. - The core view resolver provided by Spring is the
InternalResourceViewResolver; it is the default view resolver.
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver(){
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views");
resolver.setSuffix(".jspx" );
resolver.setRequestContextAttribute("requestContext");
return resolver;
}
}