MySQL Delete
To delete data from a table, DELETE statement is used. Once data is deleted from your tables you can’t recover it. It is gone. It is recommended to back up your database regularly so that if data is gone you can still recover it from your backups.
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
The WHERE clause is optional but if it’s omitted then all rows will be deleted.
Here is an example of DELETE where we are deleting customer with id 21.
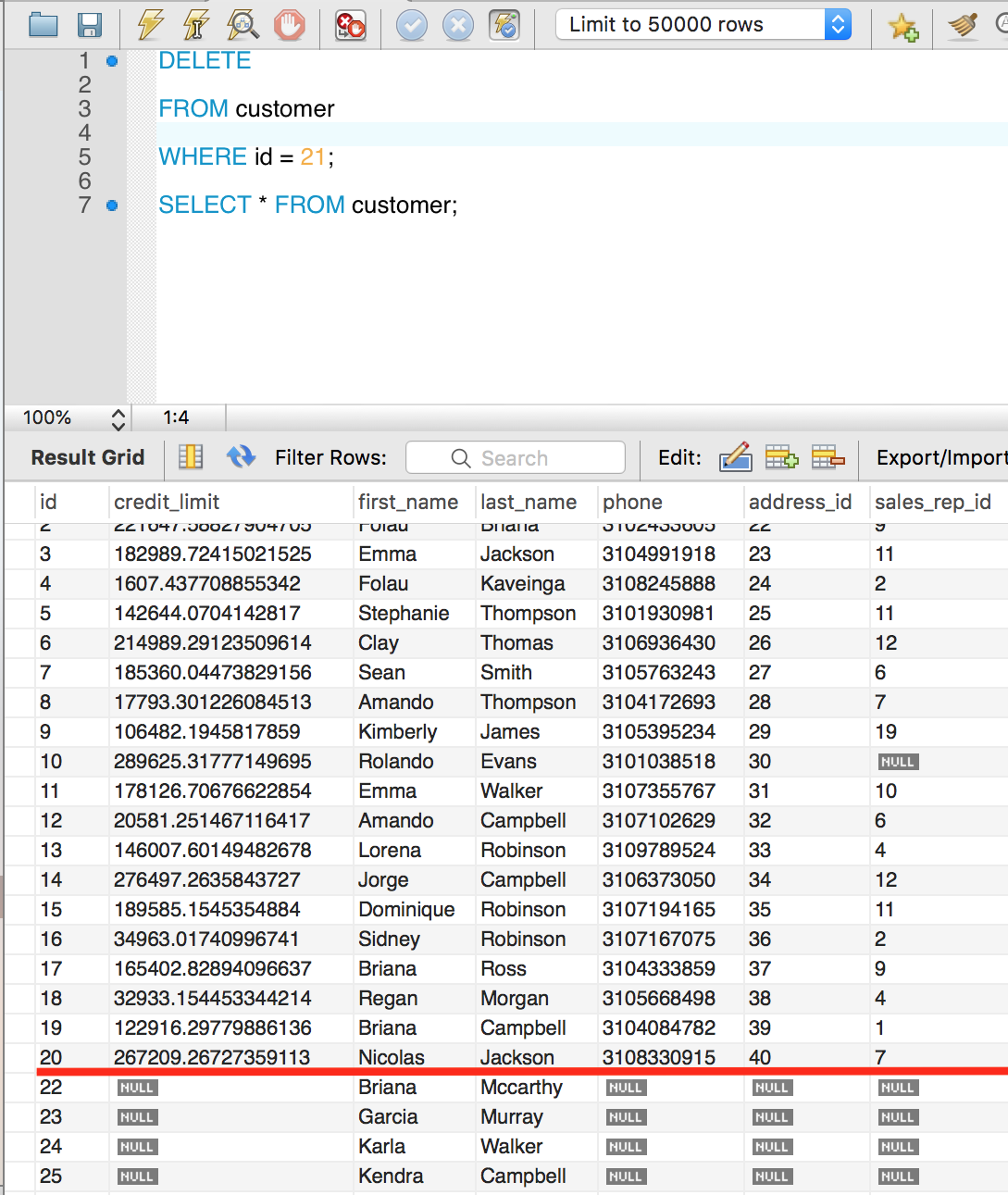
As you can see row 21st is gone. The DELETE statement returns the number of rows deleted.
To delete all rows within a table, use the TRUNCATE command which has better performance.
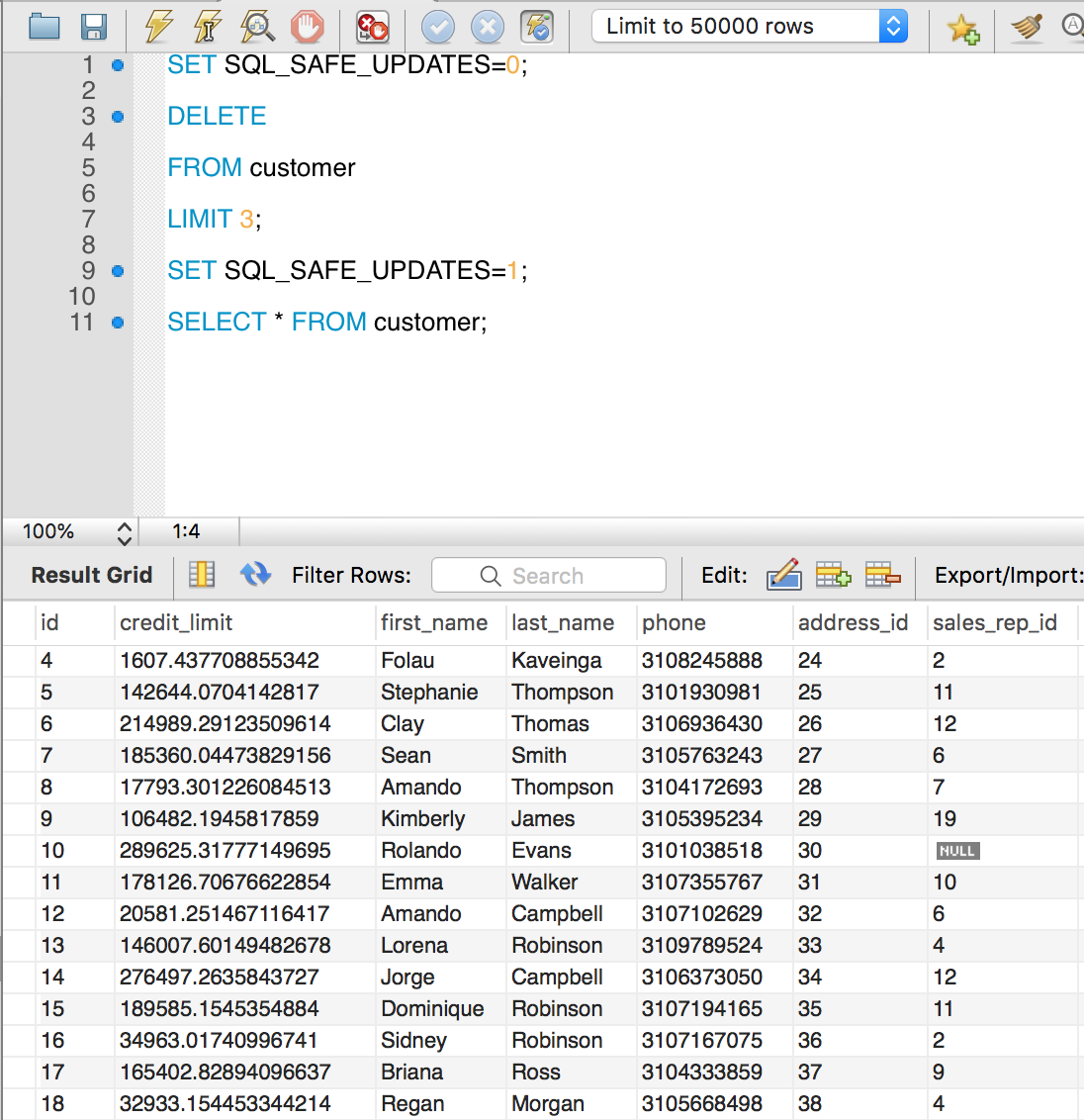
DELETE with LIMIT
When deleting data it is recommended to turn off SQL_SAFE_UPDATES.
DELETE FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name LIMIT count;
DELETE with ON CASCADE
ON DELETE CASCADE is used to delete rows or data in a child table when a row is deleted in the parent table.
You have to create your child table with it.
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_names...
FOREIGN KEY (FK)
REFERENCES parent_table_name (FK)
ON DELETE CASCADE
);
Here is the query to show which tables use ON DELETE CASCADE.
USE information_schema;
SELECT
table_name
FROM
referential_constraints
WHERE
constraint_schema = 'database_name'
AND referenced_table_name = 'parent_table'
AND delete_rule = 'CASCADE'