Elasticsearch Search API
You can search data in Elasticsearch by sending a get request with query string as a parameter or post a query in the message body of post request. A search query, or query, is a request for information about data in Elasticsearch data streams or indices.
GET doctor_ut/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
String indexName = Index.DOCTOR_UT.name().toLowerCase();
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("addresses.state.keyword", "UT"));
int from = 1;
int size = 1000;
searchSourceBuilder.from(from);
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// with sorting
// log.info("{\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(),
// searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
SearchResponse searchResponse = null;
try {
searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
log.info("search got response from elastic!, totalHits={}, maxScore={}, hitLength={}", searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value, searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore(),searchResponse.getHits().getHits().length);
Iterator<SearchHit> it = searchResponse.getHits().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SearchHit searchHit = it.next();
try {
// log.info(searchHit.getSourceAsString());
DoctorIndex doctorIndex = ObjectUtils.getObjectMapper().readValue(searchHit.getSourceAsString(), DoctorIndex.class);
log.info("doctorIndex={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(doctorIndex));
// ObjectUtils.getObjectMapper().writeValue(new FileOutputStream("output-2.json", true),
// doctorIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
By default, the Search API returns the top 10 matching documents.
To paginate through a larger set of results, you can use the search API’s size and from parameters. The size parameter is the number of matching documents to return. The from parameter is a zero-indexed offset from the beginning of the complete result set that indicates the document you want to start with.
By default, you cannot page through more than 10,000 documents using the from and size parameters. This limit is set using the index.max_result_window index setting.
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("addresses.state.keyword", "UT"));
int from = 1;
int size = 1000;
searchSourceBuilder.from(from);
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);
GET doctor_ut/_search
{
"from": 5,
"size": 5,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
The Scroll API can be used to retrieve a large number of results from a search request.
While a search request returns a single “page” of results, the scroll API can be used to retrieve large numbers of results (or even all results) from a single search request, in much the same way as you would use a cursor on a traditional database.
Scrolling is not intended for real time user requests, but rather for processing large amounts of data, e.g. in order to reindex the contents of one data stream or index into a new data stream or index with a different configuration.
The scroll API requires a scroll ID. To get a scroll ID, submit a search API request that includes an argument for the scroll query parameter . The scroll parameter indicates how long Elasticsearch should retain the search context for the request.
The search response returns a scroll ID in the _scroll_id response body parameter. You can then use the scroll ID with the scroll API to retrieve the next batch of results for the request.
You can also use the scroll API to specify a new scroll parameter that extends or shortens the retention period for the search context.
The scroll API returns the same response body as the search API.
GET doctor_ut/_search/scroll
{
"scroll_id" : "DXF1ZXJ5QW5kRmV0Y2gBAAAAAAAAAD4WYm9laVYtZndUQlNsdDcwakFMNjU1QQ=="
}
final Scroll scroll = new Scroll(TimeValue.timeValueMinutes(1L));
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
searchRequest.scroll(scroll);
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.size(1000);
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("addresses.state.keyword", "UT"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("search got response from elastic!, totalHits={}, maxScore={}, hitLength={}", searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value, searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore(),
searchResponse.getHits().getHits().length);
// process searchResponse
String scrollId = searchResponse.getScrollId();
SearchHit[] searchHits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
while (searchHits != null && searchHits.length > 0) {
SearchScrollRequest scrollRequest = new SearchScrollRequest(scrollId);
scrollRequest.scroll(scroll);
searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.scroll(scrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("search got response from elastic!, totalHits={}, maxScore={}, hitLength={}", searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value, searchResponse.getHits().getMaxScore(),
searchResponse.getHits().getHits().length);
// process searchResponse
scrollId = searchResponse.getScrollId();
searchHits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
}
ClearScrollRequest clearScrollRequest = new ClearScrollRequest();
clearScrollRequest.addScrollId(scrollId);
ClearScrollResponse clearScrollResponse = restHighLevelClient.clearScroll(clearScrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
boolean succeeded = clearScrollResponse.isSucceeded();
Full Body Search
You should use the request body search API because most parameters are passed in the HTTP request body instead of in the query string with the GET request.
Request body search not only handles the query itself, but also allows you to return highlighted snippets from your results, aggregate analytics across all results or subsets of results, and return did-you-mean suggestions, which will help guide your users to the best results quickly.
POST /_search
{
"from": 30,
"size": 10
}
Multiple Query Clauses
Query clauses are simple building blocks that can be combined with each other to create complex queries.
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "email": "folau@gmail.com" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "name": "folau" }},
"should": { "match": { "lastName": "kaveinga" }}
} }
It is important to note that a compound clause can combine any other query clauses, including other compound clauses. This means that compound clauses can be nested within each other, allowing the expression of very complex logic.
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "email": "folau@gmail.com" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "starred": true }},
{ "bool": {
"must": { "folder": "inbox" }},
"must_not": { "spam": true }}
}}
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
Queries and Filters
A filter asks a yeso r no question of every document and is used for fields that contain exact values. For examples:
- Does the status field contain the term published?
- Is the lat_lon field within 10km of a specified point?
The goal of filters is to reduce the number of documents that have to be examined by the query.
A query is similar to a filter, but also asks the question: How well does this document match?
- Best matching the words full text search
- Containing the word run, but maybe also matching runs, running, jog, or sprint
A query calculates how relevant each document is to the query, and assigns it a relevance _score, which is later used to sort matching documents by relevance. This concept of relevance is well suited to full-text search, where there is seldom a completely “correct” answer.
Queries have to not only find matching documents, but also calculate how relevant each document is, which typically makes queries heavier than filters. Also, query results are not cachable.
The match_all query simply matches all documents. It is the default query that is used if no query has been specified. It returns all rows and columns.
{
"match_all": {}
}
The match query should be the standard query that you reach for whenever you want to query for a full-text or exact value in almost any field.
If you run a match query against a full-text field, it will analyze the query string by using the correct analyzer for that field before executing the search
{
"match": {
"email": "folau"
}
}
If you use it on a field containing an exact value, such as a number, a date, a Boolean, or a not_analyzed string field, then it will search for that exact value
Note that for exact-value searches, you probably want to use a filter instead of a query, as a filter will be cached.
The match query does not use a query syntax like +user_id:2 +tweet:search. It just looks for the words that are specified. This means that it is safe to expose to your users via a search field; you control what fields they can query, and it is not prone to throwing syntax errors.
match_phrase query analyzes the text and creates a phrase query out of the analyzed text.
@Test
void searchWithMatchPhrase() {
String description = "His biggest fear";
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* match query is like contain in mysql
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchPhraseQuery("description", description));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
multi_match query builds on the match query to allow multi-field queries. Use * to query against all fields. Note that * will not query against nested fields.
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "full text search",
"fields": ["title","body"]
}
}
@Test
void searchWithMultiMatchAllFields() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* match query is like contain in mysql<br>
* * means all fields<br>
* Isabell - firstName of a diff user <br>
* 3102060312 - phoneNumber of a diff user<br>
* biggest fear - description of a diff user<br>
*/
//searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("Isabell 3102060312 biggest fear", "*"));
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("Best Buy", "*"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
You can use the term query to find documents based on a precise value such as a price, a product ID, or a username.
To better search text fields, the match query also analyzes your provided search term before performing a search. This means the match query can search text fields for analyzed tokens rather than an exact term.
The term query does not analyze the search term. The term query only searches for the exact term you provide. This means the term query may return poor or no results when searching text fields.
@Test
void searchWithTerm() {
String firstName = "Isabell";
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* term query looks for exact match. Use keyword
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("firstName.keyword", firstName));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
void searchWithTermAndMultiValues() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* term query looks for exact match. Use keyword
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termsQuery("firstName.keyword", "Leland","Harmony","Isabell"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Return documents that has a value for a field.
GET elasticsearch_learning/_search
{
"query":{
"exists" : {
"field" : "firstName",
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
@Test
void searchWithExistQuery() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* term query looks for exact match. Use keyword
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.existsQuery("firstName"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Returns documents that have terms matching a wildcard pattern.
GET elasticsearch_learning/_search
{
"query":{
"wildcard" : {
"firstName" : {
"wildcard" : "H*y",
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
}
@Test
void searchWithWildcardQuery() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
/**
* Filter<br>
* term query looks for exact match. Use keyword<br>
* These matching terms can include Honey, Henny, or Horsey.<br>
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.wildcardQuery("firstName", "H*y"));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Returns documents that contain terms matching a regular expression.
The performance of the regexp query can vary based on the regular expression provided. To improve performance, avoid using wildcard patterns, such as .* or .*?+, without a prefix or suffix.
GET elasticsearch_learning/_search
{
"query":{
"regexp" : {
"firstName" : {
"value" : "S.e",
"flags_value" : 255,
"case_insensitive" : true,
"max_determinized_states" : 10000,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
}
/**
* https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-regexp-query.html<br>
* https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/regexp-syntax.html
*/
@Test
void searchWithRegexQuery() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName","description"}, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query<br>
* Sydnee<br>
* . means match any character.<br>
* * Repeat the preceding character zero or more times.<br>
*/
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.regexpQuery("firstName", "S.*e")
.flags(RegexpQueryBuilder.DEFAULT_FLAGS_VALUE)
.caseInsensitive(true));
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
The bool query, like the bool filter, is used to combine multiple query clauses. However, there are some differences. Remember that while filters give binary yes/no answers, queries calculate a relevance score instead. The bool query combines the _score from each must or should clause that matches. This query accepts the following parameters:
must
Clauses that must match for the document to be included.
must_not
Clauses that must not match for the document to be included.
should
If these clauses match, they increase the _score; otherwise, they have no effect. They are simply used to refine the relevance score for each document.
The bool query takes a more-matches-is-better approach, so the score from each matching must or should clause will be added together to provide the final _score for each document.
The following query finds documents whose title field matches the query string how to make millions and that are not marked as spam. If any documents are starred or are from 2014 onward, they will rank higher than they would have otherwise. Documents that match both conditions will rank even higher.
GET elasticsearch_learning/_search
{
"query":{
"bool" : {
"must" : [
{
"match" : {
"firstName" : {
"query" : "Leland",
"operator" : "OR",
"prefix_length" : 0,
"max_expansions" : 50,
"fuzzy_transpositions" : true,
"lenient" : false,
"zero_terms_query" : "NONE",
"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"filter" : [
{
"match" : {
"firstName" : {
"query" : "Leland",
"operator" : "OR",
"prefix_length" : 0,
"max_expansions" : 50,
"fuzzy_transpositions" : true,
"lenient" : false,
"zero_terms_query" : "NONE",
"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"must_not" : [
{
"match" : {
"firstName" : {
"query" : "Leilani",
"operator" : "OR",
"prefix_length" : 0,
"max_expansions" : 50,
"fuzzy_transpositions" : true,
"lenient" : false,
"zero_terms_query" : "NONE",
"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"should" : [
{
"match" : {
"firstName" : {
"query" : "Lelanddd",
"operator" : "OR",
"prefix_length" : 0,
"max_expansions" : 50,
"fuzzy_transpositions" : true,
"lenient" : false,
"zero_terms_query" : "NONE",
"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
@Test
void searchWithBooleanQuery() {
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 10;
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(database);
searchRequest.allowPartialSearchResults(true);
searchRequest.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.from(pageNumber * pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.size(pageSize);
searchSourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
/**
* fetch only a few fields
*/
// searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(new String[]{ "id", "firstName", "lastName", "cards" }, new String[]{""});
/**
* Query
*/
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
/**
* Filter<br>
* term query looks for exact match. Use keyword
*/
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("firstName", "Leland"));
boolQuery.mustNot(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("firstName", "Leilani"));
boolQuery.should(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("firstName", "Lelanddd"));
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("firstName", "Leland"));
searchSourceBuilder.query(boolQuery);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
searchRequest.preference("firstName");
if (searchSourceBuilder.sorts() != null && searchSourceBuilder.sorts().size() > 0) {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}, \"sort\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString(), searchSourceBuilder.sorts().toString());
} else {
log.info("\n{\n\"query\":{}\n}", searchSourceBuilder.query().toString());
}
try {
SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("isTimedOut={}, totalShards={}, totalHits={}", searchResponse.isTimedOut(), searchResponse.getTotalShards(), searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);
List<User> users = getResponseResult(searchResponse.getHits());
log.info("results={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(users));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Note that if there are no must clauses, at least one should clause has to match. However, if there is at least one must clause, no should clauses are required to match.
Combine Queries with Filters
Use bool query to combine query and filter.
How a query works under the hood
Let’s assume you have 3 nodes.
#Query Phase
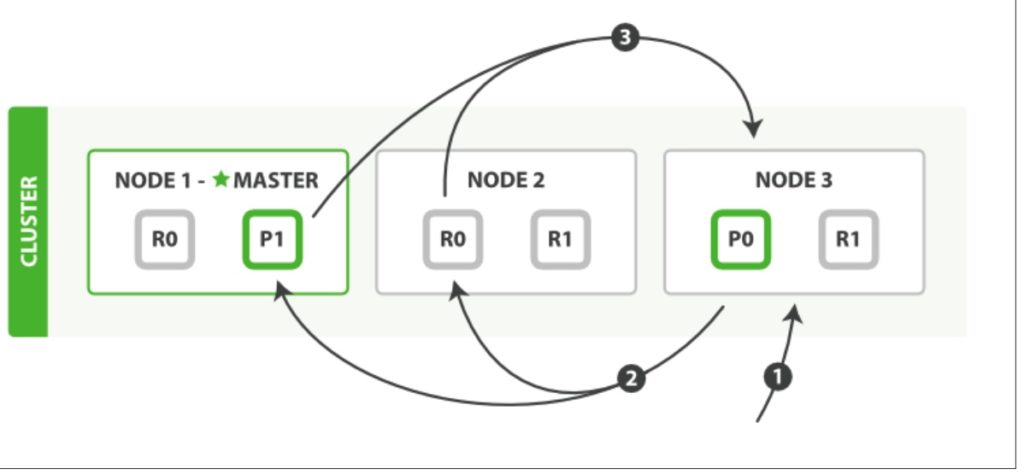
- The client sends a search request to Node 3, which creates an empty priority queue of size from + size.
- Node 3 forwards the search request to a primary or replica copy of every shard in the index. Each shard executes the query locally and adds the results into a local sorted priority queue of size from + size.
- Each shard returns the doc IDs and sort values of all the docs in its priority queue to the coordinating node, Node 3, which merges these values into its own priority queue to produce a globally sorted list of results.
When a search request is sent to a node, that node becomes the coordinating node. It is the job of this node to broadcast the search request to all involved shards, and to gather their responses into a globally sorted result set that it can return to the client.
The first step is to broadcast the request to a shard copy of every node in the index. Just like document GET requests, search requests can be handled by a primary shard or by any of its replicas. This is how more replicas (when combined with more hard‐ ware) can increase search throughput. A coordinating node will round-robin through all shard copies on subsequent requests in order to spread the load.
Each shard executes the query locally and builds a sorted priority queue of length from + size—in other words, enough results to satisfy the global search request all by itself. It returns a lightweight list of results to the coordinating node, which con‐ tains just the doc IDs and any values required for sorting, such as the _score.
The coordinating node merges these shard-level results into its own sorted priority queue, which represents the globally sorted result set. Here the query phase ends.
An index can consist of one or more primary shards, so a search request against a single index needs to be able to combine the results from multiple shards. A search against multiple or all indi‐ ces works in exactly the same way—there are just more shards involved.
#Fetch Phase
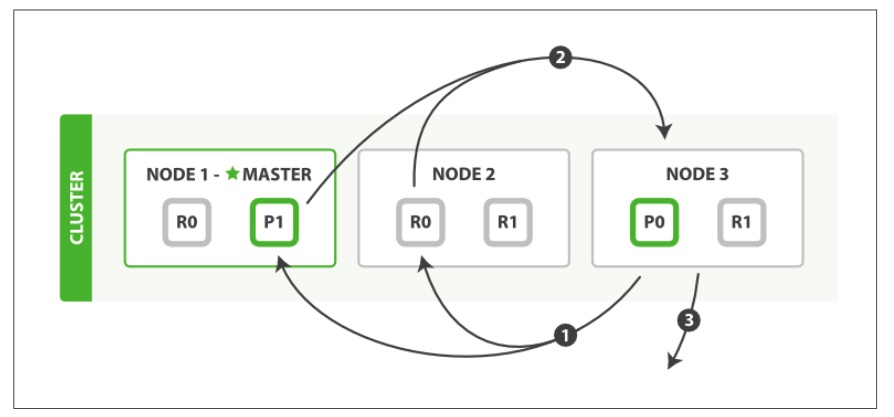
- The coordinating node identifies which documents need to be fetched and issues a multi GET request to the relevant shards.
- Each shard loads the documents and enriches them, if required, and then returns the documents to the coordinating node.
- Once all documents have been fetched, the coordinating node returns the results to the client.
The coordinating node first decides which documents actually need to be fetched. For instance, if our query specified { “from”: 90, “size”: 10 }, the first 90 results would be discarded and only the next 10 results would need to be retrieved. These documents may come from one, some, or all of the shards involved in the original search request.
The coordinating node builds a multi-get request for each shard that holds a perti‐ nent document and sends the request to the same shard copy that handled the query phase.
The shard loads the document bodies—the _source field—and, if requested, enriches the results with metadata and search snippet highlighting. Once the coordinating node receives all results, it assembles them into a single response that it returns to the client.
Bouncing Result
Imagine that you are sorting your results by a timestamp field, and two documents have the same timestamp. Because search requests are round-robined between all available shard copies, these two documents may be returned in one order when the request is served by the primary, and in another order when served by the replica. This is known as the bouncing results problem: every time the user refreshes the page, the results appear in a different order. The problem can be avoided by always using the same shards for the same user, which can be done by setting the preference parameter to an arbitrary string like the user’s session ID.