Java interview – OOP
1.What is Object-oriented Programming?
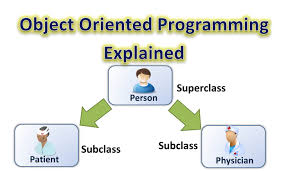
Object-oriented programming is a programming model or approach where the programs you create are organized around objects rather than logic and functions. The states and behaviors of an object are represented as member variables and methods. This approach is ideal for the programs that are large and complex and need to be actively updated or maintained. Here below is an example of OOP where this little piece is focused on Person. There can be other entities like payment method, Account, etc. Programs are organized into entities.
2. What are the advantages of OOPs?
Simplicity: Domain models or entities are modeled after real-world objects. It is easier to understand and to relate to. The program structure is also easier to comprehend.
Modularity: Each object is decoupled from other objects of the system.
Modifiability: It is easy to make minor changes in the data or the functionalities in an OO program. Changes inside a class do not affect any other part of a program since the only public interface that the external world has to a class is through the use of methods.
Extensibility: Adding new features or responding to changing operating environments can be solved by introducing a few new objects and modifying some existing ones.
Maintainability: Objects can be maintained separately, making locating and fixing problems easier.
Reusability: Objects can be reused in different programs.
3. What is the difference between procedural programming and OOPs?
- Procedural language is based on functions but object oriented language is based on real world objects.
- Procedural language gives importance on the sequence of function execution but object oriented language gives importance on states and behaviors of the objects.
- Procedural language exposes the data to the entire program but object oriented language encapsulates the data.
- Procedural language follows top down programming paradigm but object oriented language follows bottom up programming paradigm.
- Procedural language is complex in nature so it is difficult to modify, extend and maintain but object oriented language is less complex in nature so it is easier to modify, extend and maintain.
- Procedural language provides less scope of code reuse but object oriented language provides more scope of code reuse.
4. What are the core concepts of OOPs?
- Inheritance: Inheritance is a process where one class acquires the properties and functionalities of another.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping up the data and code together as a single unit.
- Abstraction: Abstraction is the methodology of hiding the implementation details from the user and only providing the functionality to the users.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism is the ability of a variable, function or object to take multiple forms.
- Composition
- Association
- Aggregation
-
Classes and Objects:
- Classes are the blueprint or template that defines the structure and behavior of objects. They encapsulate data and methods.
- Objects are instances of classes. They represent specific entities that have state (data) and behavior (methods).
-
Encapsulation:
- Encapsulation is the process of bundling data (attributes/fields) and methods that operate on the data within a single unit, i.e., a class.
- It provides data hiding, where the internal implementation details of a class are hidden from the outside world, and access to the data is controlled through methods.
- Encapsulation helps maintain data integrity, improves code organization, and facilitates modularity and reusability.
-
Inheritance:
- Inheritance allows a class to inherit the properties (fields and methods) of another class, known as the superclass or parent class.
- The class that inherits the properties is called the subclass or child class.
- Inheritance promotes code reuse, allows for the creation of specialized classes from a general superclass, and supports the concept of polymorphism.
-
Polymorphism:
- Polymorphism means the ability of objects of different classes to respond to the same method invocation in different ways.
- Polymorphism in Java is achieved through method overriding (runtime polymorphism) and method overloading (compile-time polymorphism).
- Method overriding allows a subclass to provide a different implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass.
- Method overloading allows multiple methods with the same name but different parameters to be defined in the same class.
-
Abstraction:
- Abstraction is the process of representing complex real-world entities as simplified models in code.
- Abstract classes and interfaces are used to achieve abstraction in Java.
- Abstract classes are classes that cannot be instantiated but can be used as base classes for subclasses. They can have abstract methods (without implementation) and concrete methods.
- Interfaces define a contract of methods that a class must implement. They provide a way to achieve multiple inheritance and allow for programming to interfaces.
5. What is the difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation?
- “Program to interfaces, not implementations” is the principle for Abstraction and “Encapsulate what varies” is the OO principle for Encapsulation.
- Abstraction provides a general structure of a class and leaves the details for the implementers. Encapsulation is to create and define the permissions and restrictions of an object and its member variables and methods.
- Abstraction is implemented in Java using interface and abstract class while Encapsulation is implemented using four types of access level modifiers: public, protected, no modifier and private.
Abstraction:
- Abstraction is a concept that focuses on representing complex real-world entities as simplified models in code.
- It involves the process of identifying and extracting essential features and behavior of an entity, while ignoring unnecessary details.
- Abstraction allows you to create abstract classes and interfaces in Java.
- Abstract classes are classes that cannot be instantiated but can be used as base classes for subclasses. They can have both abstract methods (without implementation) and concrete methods.
- Interfaces define a contract of methods that a class must implement.
- Abstraction provides a way to define common behavior and establish a hierarchy of classes, where higher-level classes provide a more general abstraction while lower-level classes provide more specific implementations.
- It allows you to work with objects at a higher level of abstraction, focusing on what an object does rather than how it does it.
- Abstraction simplifies complex systems by breaking them down into manageable and understandable units.
Encapsulation:
- Encapsulation is a concept that focuses on bundling data (attributes/fields) and methods that operate on the data within a single unit, i.e., a class.
- It involves hiding the internal implementation details of a class and exposing only necessary information through methods.
- Encapsulation provides data hiding, where the internal state of an object is not directly accessible or modifiable from outside the class.
- It protects the integrity of the data by controlling access to it through methods, allowing the class to enforce rules and validations.
- Encapsulation helps in achieving modularity, as the internal implementation of a class can be modified without affecting other parts of the code that use the class.
- It improves code organization, as related data and behavior are encapsulated within a single class, making the code more maintainable and understandable.
- Encapsulation also facilitates code reuse, as objects can be used as black boxes, interacting with other objects through well-defined interfaces.
Abstraction focuses on representing complex entities as simplified models, while encapsulation focuses on bundling data and methods within a class, controlling access to the data, and hiding the implementation details. Abstraction provides a higher-level view, emphasizing what an object does, while encapsulation provides information hiding and modular code organization. Both concepts are crucial for building robust and maintainable object-oriented programs.
6. What is the diamond problem in inheritance?
In the case of multiple inheritances, suppose class A has two subclasses B and C, and class D has two superclasses B and C. If a method present in A is overridden by both B and C but not by D then from which class D will inherit that method B or C? This problem is known as the diamond problem.
7. Why Java does not support multiple inheritances?
Java was designed to be a simple language and multiple inheritances introduce complexities like the diamond problem. Inheriting states or behaviors from two different types of classes is a case which in reality very rare and it can be achieved easily through an object association.
8. What is Static Binding and Dynamic Binding?
Static or early binding is resolved at compile time. Method overloading is an example of static binding. Static binding is faster than dynamic binding.
Dynamic or late or virtual binding is resolved at run time. Method overriding is an example of dynamic binding. This decision making during runtime makes Dynamic binding slower than static binding.
9. What is the meaning of the “IS-A” and “HAS-A” relationship?
“IS-A” relationship implies inheritance. A subclass object is said to have an “IS-A” relationship with the superclass or interface. If class A extends B then A “IS-A” B. It is transitive, that is, if class A extends B and class B extends C then A “IS-A” C. The “instance of” operator in java determines the “IS-A” relationship.
When a class A has a member reference variable of type B then A “HAS-A” B. It is also known as Aggregation.
10. What is an Association?
Association is a relationship between two objects with multiplicity.
11. What is Aggregation?
Aggregation is also known as “HAS-A” relationship. When class Car has a member reference variable of type Wheel then the relationship between the classes Car and Wheel is known as Aggregation. Aggregation can be understood as “whole to its parts” relationship.
Car is the whole and wheel is part. The wheel can exist without the Car. Aggregation is a weak association.
12. What is Composition?
Composition is a special form of Aggregation where the part cannot exist without the whole. Composition is a strong Association. Composition relationship is represented like aggregation with one difference that the diamond shape is filled.
13. What is Dependency?
When one class depends on another because it uses that class at some point in time then this relationship is known as Dependency. One class depends on another if the independent class is a parameter variable or local variable of a method of the dependent class. A Dependency is drawn as a dotted line from the dependent class to the independent class with an open arrowhead pointing to the independent class.
14. What is the difference between Association and Dependency?
The main difference between Association and Dependency is in case of Association one class has an attribute or member variable of the other class type but in case of Dependency a method takes an argument of the other class type or a method has a local variable of the other class type.
15. 30 commonly asked interview questions related to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
-
Question: What is the difference between a class and an object in Java? Answer: A class is a blueprint or template that defines the structure and behavior of objects, while an object is an instance of a class. A class represents a general concept, while an object represents a specific instance of that concept.
-
Question: Explain the concept of inheritance in Java. Answer: Inheritance allows a class to inherit the properties (fields and methods) of another class, known as the superclass or parent class. It promotes code reuse and allows for the creation of specialized classes from a general superclass. Example: A
Carclass can inherit common properties and methods from aVehicleclass. -
Question: What is the difference between method overloading and method overriding? Answer: Method overloading is the process of defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters within the same class. Method overriding, on the other hand, occurs when a subclass provides a different implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass.
-
Question: What is the purpose of the
superkeyword in Java? Answer: Thesuperkeyword is used to refer to the immediate parent class’s members (fields and methods) from within a subclass. It is often used to call the superclass’s constructor or to access overridden methods or hidden fields. -
Question: What is the concept of polymorphism in Java? Answer: Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common superclass, enabling them to respond to the same method invocation in different ways. Polymorphism is achieved through method overriding (runtime polymorphism) and method overloading (compile-time polymorphism).
-
Question: Explain the concept of encapsulation in Java. Answer: Encapsulation is the process of bundling data (attributes/fields) and methods that operate on the data within a single unit, i.e., a class. It provides data hiding, where the internal implementation details of a class are hidden from the outside world, and access to the data is controlled through methods.
-
Question: What is an abstract class in Java? How is it different from an interface? Answer: An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated but can be used as a base class for subclasses. It can have both abstract methods (without implementation) and concrete methods. An interface, on the other hand, defines a contract of methods that a class must implement. Unlike an abstract class, an interface cannot contain implementation details.
-
Question: What is the purpose of the
finalkeyword in Java? Answer: Thefinalkeyword is used to restrict the behavior of classes, methods, and variables. A final class cannot be subclassed, a final method cannot be overridden, and a final variable cannot be reassigned once initialized. -
Question: What is the concept of method overriding in Java? Answer: Method overriding occurs when a subclass provides a different implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass. The overridden method in the subclass must have the same signature (name, return type, and parameters) as the method in the superclass.
-
Question: What is the purpose of the
thiskeyword in Java? Answer: Thethiskeyword refers to the current instance of a class. It is often used to differentiate between instance variables and method parameters or to invoke constructors within a class. -
Question: What is the difference between composition and inheritance? Answer: Composition represents a “has-a” relationship, where one class contains references to objects of another class. Inheritance, onContinuing from the previous response, here are more interview questions related to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java:
-
Question: What is the concept of method overloading in Java? Answer: Method overloading is the process of defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters within the same class. The compiler determines which method to invoke based on the number, types, and order of the arguments passed.
-
Question: What is the difference between abstract classes and interfaces in Java? Answer: Abstract classes can have both abstract and concrete methods, while interfaces can only have abstract methods. A class can implement multiple interfaces, but it can only extend one abstract class.
-
Question: What is the significance of the
statickeyword in Java? Answer: Thestatickeyword is used to define class-level members that are shared among all instances of a class.staticmethods and variables can be accessed without creating an instance of the class. -
Question: What is the purpose of the
finalkeyword for variables in Java? Answer: Thefinalkeyword for variables makes them constants, meaning their values cannot be changed once assigned. It is used to create immutable variables. -
Question: What is the concept of method hiding in Java? Answer: Method hiding occurs when a subclass defines a static method with the same name and signature as a static method in its superclass. The subclass’s static method hides the superclass’s static method.
-
Question: What is the difference between shallow copy and deep copy? Answer: Shallow copy creates a new object that references the same memory as the original object, while deep copy creates a new object with its own memory, copying all the values of the original object.
-
Question: How does Java support multiple inheritance? Answer: Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance of classes, but it supports multiple inheritance of interfaces. By implementing multiple interfaces, a class can inherit multiple sets of behavior.
-
Question: What are access modifiers in Java, and what is their significance? Answer: Access modifiers control the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and variables. They include
public,protected,private, and default (no modifier). They ensure proper encapsulation and provide control over the accessibility of code. -
Question: What is a static initializer block in Java? Answer: A static initializer block is a block of code that is executed when a class is loaded into memory. It is used to initialize static variables or perform one-time setup tasks for the class.
-
Question: What is the purpose of the
instanceofoperator in Java? Answer: Theinstanceofoperator is used to check if an object is an instance of a particular class or implements a specific interface. It returns a boolean value indicating the result of the check. -
Question: What are accessors and mutators (getters and setters) in Java? Answer: Accessors (getters) are methods used to retrieve the values of private fields, while mutators (setters) are methods used to modify the values of private fields. They ensure controlled access to the object’s state.
-
Question: What is the purpose of the
clone()method in Java? Answer: Theclone()method is used to create a copy of an object. It performs a shallow copy by default, but it can be overridden to perform a deep copy if necessary. -
Question: What is the
equals()method in Java used for? Answer: Theequals()method is used to compare the equality of two objects. It is typically overridden to provide a custom implementation for object comparison based on specific criteria. -
Question: What is the difference between
String,Continuing from the previous response, here are more interview questions related to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java: -
Question: What is the difference between
String,StringBuilder, andStringBufferin Java? Answer:Stringis an immutable class, meaning its value cannot be changed once created. It is suitable for situations where the value needs to remain constant.StringBuilderandStringBufferare mutable classes that can be used to manipulate strings.StringBuilderis not thread-safe, whileStringBufferis thread-safe due to its synchronized methods.
-
Question: What is method hiding in Java, and how does it differ from method overriding? Answer: Method hiding occurs when a subclass defines a static method with the same name and signature as a static method in its superclass. The subclass’s static method hides the superclass’s static method. Method overriding, on the other hand, occurs when a subclass provides a different implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass.
-
Question: What is the difference between the
throwandthrowskeywords in Java? Answer:- The
throwkeyword is used to explicitly throw an exception within a method or block of code. - The
throwskeyword is used in a method signature to indicate that the method may throw one or more exceptions. It is used for checked exceptions.
- The
-
Question: What is the
finalize()method in Java used for? Answer: Thefinalize()method is a method of theObjectclass that is called by the garbage collector when it determines that there are no more references to the object. It can be overridden to perform cleanup tasks before the object is garbage collected. -
Question: What is the difference between the
ArrayListandLinkedListclasses in Java? Answer:ArrayListis implemented as a dynamic array, providing fast random access and iteration. It is suitable for scenarios where frequent element access and modification are required.LinkedListis implemented as a doubly-linked list, providing fast insertion and deletion at both ends. It is suitable for scenarios where frequent insertions and deletions are required.