Hasura – Authentication
Handling authentication correctly is a key step in ensuring the security of your application in production. This is a very important component of any backend system. There are multiple ways to be authenticated but in this post I will focus on JWT authentication.
Ways to authenticate users for your application:
- JSON web tokens (JWT) based authentication: Use this method if you are authenticating your end-users using a JWT based authentication provider like Auth0 or Firebase or AWS Cognito.
- Webhook based authentication: Use this method if you need to roll out a custom authentication solution.
- Unauthenticated access: Use this method if you want to provide anonymous access to some data, for example if you want to make a public feed of events.
- Admin secret based authentication: Use this method if you are doing server to server communication and the client is a trusted client.
JWT based authentication
We assume you are familiar with what a JWT is. If you are new to JWT’s here is a guide we have put together explaining how JWT’s work in the context of front end GraphQL clients. It also covers the security aspects of using a JWT for authentication.
Here’s how JWT based authentication works:
- An end-user is authenticated to the app by your authentication server(sign up or sign in)
- On successful authentication, the authentication server returns a JWT to the app with the user and role information embedded in the claims section
- On subsequent calls to Hasura, app passes the JWT in the
Authorizationheader. - Hasura validates the token and extracts the user and role information
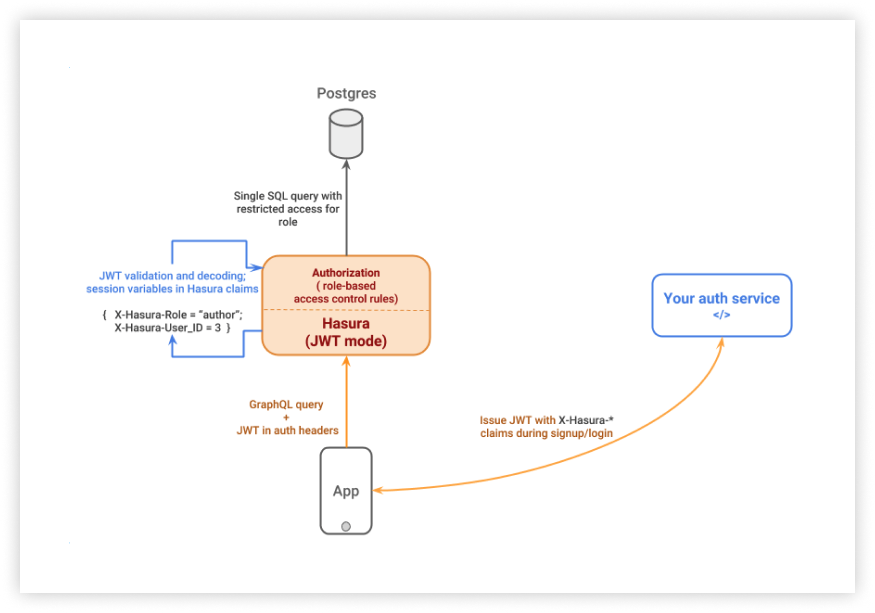
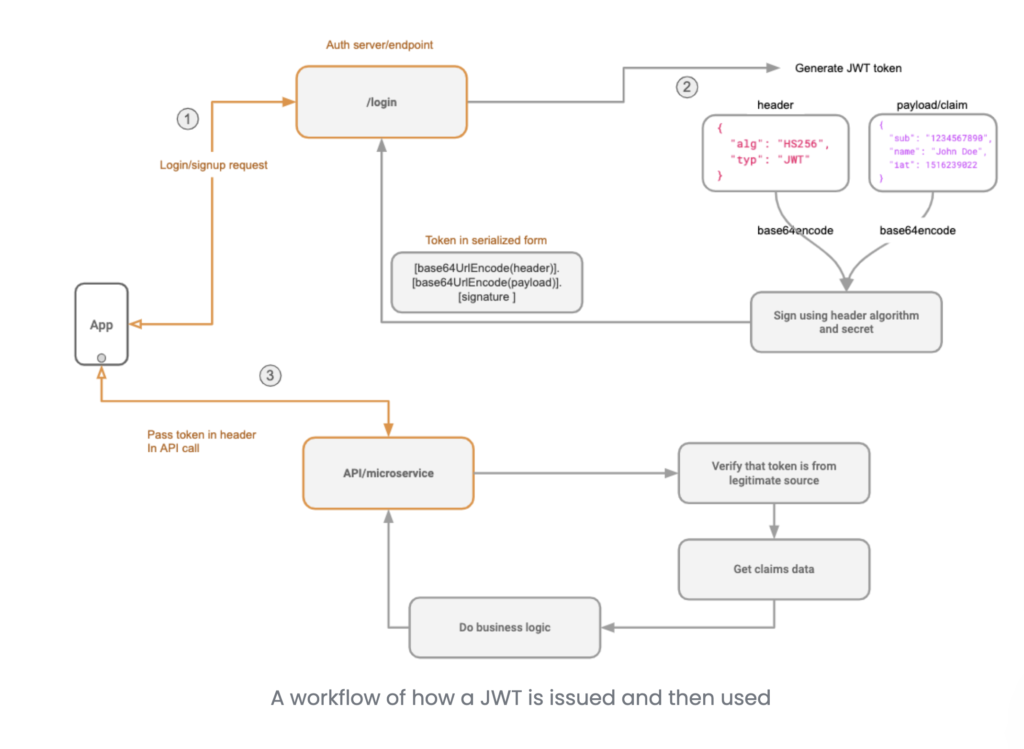
Validating the JWT Token in step 4. above requires a JWT secret. You can enable JWT mode by using the --jwt-secret flag or HASURA_GRAPHQL_JWT_SECRET environment variable while starting Hasura. The the value of the flag or environment variable must be a JSON object.
{
"type":"HS256",
"key":"testtesttesttesttesttesttesttest",
"claims_namespace":"hasura",
"audience":"folautech-api",
"issuer":"folautech-api"
}
Note that key must be equal to or more than 32 characters.
JWT Payload
{
"iss" : "folautech-api",
"jti" : "5c16f712-7ded-4479-9c90-266501b003d0-PfAdAIEeLz",
"sub" : "3",
"aud" : "folautech-meal-plan",
"iat" : "2021-03-16T09:02:12.955Z",
"exp" : "2021-03-16T10:42:12.955Z",
"admin" : false,
"name" : "Laulau Kaveinga",
"hasura" : {
"x-hasura-default-role" : "user",
"x-hasura-user-id" : "3",
"x-hasura-allowed-roles" : [ "user" ]
}
}
- A
x-hasura-default-rolefield : indicating the default role of that user i.e. the role that will be used in casex-hasura-roleheader is not passed. - A
x-hasura-allowed-rolesfield : a list of allowed roles for the user i.e. acceptable values of thex-hasura-roleheader. Thex-hasura-default-rolespecified should be a member of this list. - A
x-hasura-user-idfield : id of the authenticated user which is used to authorized user to access database tables. - A
x-hasura-customfield : you can add custom hasura properties which can be used to query database