Docker Guide
What is docker?
Getting Started
Download docker and install it on your computer
- Link to developer guide – https://docs.docker.com/ee/
- Select the docker option based on your operation system. In my case, I selected Docker for desktop mac. Then from there should be a link to download the docker executable onto your computer.
- You will have to create a docker account to download docker.
- Install docker by double-clicking on the executable your downloaded and follow instructions.
Docker commands
You are going to use the command-line interface to work with Docker.
docker images
– list out all the images in your computer
docker ps -a
– list out all the running containers on your computer
docker rmi imageId
– delete or remove an image.
docker stop containerId
– stop a running container
docker rm containerId
– delete a container
docker pull image: tag
– pull an image from a docker registry(docker hub or AWS ECR).
docker pull mysql
Run docker container automatically
Use these tags
-dit --restart unless-stopped
docker run -p outside-port:internal-port –name container-name -dit –restart unless-stopped -d image_name:image_tag
– run docker container with the port where the container will use both externally and internally, the name of the container, the image, and tag being used, and a command to make sure the container will restart if it stops.
– -d means that to run container in background and print container ID
docker run -p outside-port:internal-port --name container-name -dit --restart unless-stopped -d image_name:image_tag
docker run -p 8080:8080 --name springboot-hello-0-0-1 -dit --restart unless-stopped -d springboot-hello:0-0-1
Push up a docker image to aws docker registry
1. Login to aws ECR from your computer
aws ecr get-login-password --profile folauk110
2. Build image
docker build -t project .
3. Tag image
docker tag project:latest remote-ecr-url/project:latest
4. Push image to remote registry
docker push remote-ecr-url/project:latest
docker exec -it {container-name} sh
or
docker exec -it {container-name} sh /bin/bash
Pull redis docker image
docker pull redis
Run redis docker container
docker run --name container-redis -dit --restart unless-stopped -p 6379:6379 -d redis
Set keys and values in redis
First, ssh into the redis container.
docker exec -it container-redis sh
Second, use the redis-cli
redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> set docker great OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get docker "great" 127.0.0.1:6379> set name objectrocket OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get name "objectrocket"
Install Elasticsearch using docker
Pull elasticsearch docker image
Make sure to use the right version that your code and Kibana is using.
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.1.0
Run elasticsearch docker container
docker run -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --name elasticsearch -e "discovery.type=single-node" -dit --restart unless-stopped -d docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.1.0Add Elasticsearch Password
-e ELASTIC_PASSWORD=MagicWord
docker run -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --name elasticsearch -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ELASTIC_PASSWORD=DDloadjes233j -dit --restart unless-stopped -d docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.1.0
Pull kibana docker image
Make sure to use the right version that your code and elasticsearch is using.
docker pull docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.1.0
Run kibana docker container
docker run --link elasticsearch:elasticsearch -dit --restart unless-stopped --name kibana -p 5601:5601 docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.1.0
Access kibana locally by going on http://localhost:5601/app/kibana
Add Elasticsearch Password
# add elasticsearch password -e ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=DDloadjes233j Example docker run --link elasticsearch:elasticsearch -e ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=DDloadjes233j -dit --restart unless-stopped --name kibana -p 5601:5601 docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.1.0
# pull image docker pull docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:7.15.0 # run container docker run -dit --restart unless-stopped --name logstash -v ~/pipeline/:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline/ docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:7.15.0
docker pull docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:7.15.0
Postgresql with docker
#pull image docker pull postgres:12.6 #run docker container docker run --name postgres --restart unless-stopped -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=test -v /Users/folaukaveinga/Software/postgres/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data -d postgres:12.6
Ubuntu with docker
Sometimes when you want to play or learn linux you want to have a linux OS to play with. With docker you can pull a ubuntu docker image and run it locally.
docker pull ubuntu
Run a ubuntu container
docker run -it ubuntu /bin/bash
You will be in the root folder of the ubuntu container right away after running the above command.
docker container restart [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...] // -t or --time represents seconds to wait for stop before killing the container docker container restart -t 5 bee0a80b1424
View logs of a docker container
docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER // Follow log output -f or --follow docker logs -f asdfwers
Terminate process(PID) command
If you ever run multiple java projects (microservices) on eclipse. Most of the time you want to start them up all at the same time and luckily eclipse has this feature. Unfortunately what Eclipse doesn’t have is a way to stop or kill all of you java projects(processes) all at the same time. This is useful when you want fresh and clean instances for all my microservices and not have any process in a stale state.
To terminate all of your projects or java processes, do this:
- Open up terminal and type in this command “killall java”
- Or open terminal within your eclipse. Open Eclipse, right-click on a project in the Package Explorer panel, hover over Show in, select terminal, and type in this command “killall java”
MySQL View
Views are virtual tables what consist of columns and rows from real tables within a database. Views don’t contain the data they display. Views are practically for read-only but some databases allow updating on views.
Here is how you create a view.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column_name1, column_name2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition;
You can just JOINs if needed to generate your SELECT statement. Here is how views are created.
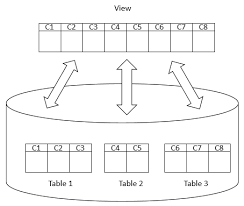
Advantages of Views
- A database view simplifies the complexity of a query. The underlying view might consist of a complex query like multiple joins and subqueries so calling a view by a simple select statement really helps reduce the code you have to write.
- A database view can have calculated columns.
- A database view can be created based off of another view.
Disadvantages of Views
- Table dependency.
- Slowness in performance if views are derived from other views.
- Views cannot have indexes. Only the underlying tables have indexes.
- If you rename a column name on the underlying table, MySQL does not throw an exception.
- Views based on complex queries such as JOINs and sub queries are not updatable. Simple select statement views are updatable.
Views and tables share the same namespace so views cannot be named the same name of an existing table.
Negotiating Salary
Spring Boot Testing
When it comes to testing, you must follow Test Driven Development principles which have great practices to keep your code and logic clean. One important thing to remember about testing, You must not include logic in your tests.
Rules of Test Driven Development
- Don’t write production code without a failing test first.
- Write only enough test code to fail.
- Write minimal test code to make the failing test pass.
Integration Testing
Integration testing allows you to spin up the server, hook up all components of your application, and you make a call to the endpoint. When this happens, you able to hit the flow of logic the endpoint is meant to execute. You can mock 3rd party api calls if you want.
For example. Let’s say you have an Activity entity. You have an endpoint that exposes a search for activities. This is how it is set up.
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@DirtiesContext
public class ControllerTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Resource
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
@Autowired
private Filter springSecurityFilterChain;
@MockBean
private UserCacheService userCacheService;
@Before
public void setUp() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(webApplicationContext).addFilters(springSecurityFilterChain).build();
ApiTokenSession apiTokenSession = new ApiTokenSession();
apiTokenSession.setPrimary(true);
apiTokenSession.setUserUuid("adminUuid");
apiTokenSession.setUserAuthorities(Arrays.asList("USER"));
apiTokenSession.setExpiredAt(DateUtils.addDays(new Date(), 1));
apiTokenSession.setDeviceId("test_agent");
when(userCacheService.findApiSessionToken("admin_token")).thenReturn(Optional.of(sideCarApiTokenSessionAdmin));
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void searchActivity_with_includes() throws Exception {
String memberUuid = "test-member-uuid-0e045fb7-038a-49e1-b49f-b0b1cec70939";
Activity activity = new Activity();
// account,member
activity.setEntityName("member");
activity.setDescription("A profile for {{entity}} was created by {{actor}}");
activity.setEntityUuid(memberUuid);
activity.setEntityLabel("Test");
activity.setType("CREATE");
activityRepository.saveAndFlush(activity);
activity = new Activity();
// account,member,expense
activity.setEntityName("member");
activity.setDescription("{{actor}} edited member {{entity}}");
activity.setEntityUuid(memberUuid);
activity.setEntityLabel("Zen Smith ASO-T");
activity.setType("EDIT");
activityRepository.saveAndFlush(activity);
activity = new Activity();
// account,member,expense
activity.setEntityName("member");
activity.setDescription("{{actor}} deleted member {{entity}}");
activity.setEntityUuid(memberUuid);
activity.setEntityLabel("Zen Smith ASO-T");
activity.setType("DELETE");
activityRepository.saveAndFlush(activity);
// @formatter:off
RequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/activity/search")
.header("token", "admin_token")
.param("entityName", "member")
.param("entityUuid", memberUuid)
.param("includeTypes", "CREATE","DELETE","EDIT")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8);
MvcResult result = this.mockMvc.perform(requestBuilder)
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andReturn();
String contentAsString = result.getResponse().getContentAsString();
CustomPage<Activity> activityResult = objectMapper.readValue(contentAsString, new TypeReference<CustomPage<Activity>>() {});
assertThat(activityResult).isNotNull();
List<Activity> activities = activityResult.getContent();
log.info("activities={}",activities);
assertThat(activities).isNotNull();
assertThat(activities.size()).isGreaterThan(0);
Optional<Activity> optActivity= activities.stream().filter(actvty -> actvty.getType().equals("CREATE") && actvty.getEntityUuid().equals(memberUuid)).findFirst();
assertThat(optActivity.isPresent()).isTrue();
optActivity= activities.stream().filter(actvty -> actvty.getType().equals("EDIT") && actvty.getEntityUuid().equals(memberUuid)).findFirst();
assertThat(optActivity.isPresent()).isTrue();
optActivity= activities.stream().filter(actvty -> actvty.getType().equals("DELETE") && actvty.getEntityUuid().equals(memberUuid)).findFirst();
assertThat(optActivity.isPresent()).isTrue();
// @formatter:on
}
}
Testing endpoints(just the controller web layer) with MockMvc and Mockito
- Use MockMvc to mock the endpoint call.
- Use @MockBean to mock service interface and Mockiot.when() method to mock service calls.
- Use mockMvc.perform to perform endpoint calls.
- Use and andExpect() method to verify endpoint response.
- Use Mockito.verify() method to verify service calls.
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(UserController.class)
public class UserRestControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testUserSave() throws Exception {
User user = new User("kinga", "kaveinga", 21, "kinga@gmail.com");
User savedUser = new User(1, "kinga", "kaveinga", 21, "kinga@gmail.com");
/**
* thenReturn or doReturn() are used to specify a value to be returned <br/>
* upon method invocation.
*/
when(userService.save(user)).thenReturn(savedUser);
this.mockMvc.perform(post("/users").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(user.toJson()))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is("kinga")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.id", is(1)));
verify(userService, times(1)).save(user);
verifyNoMoreInteractions(userService);
}
@Test
public void testGetUserById() throws Exception {
User mockUser = new User("folau", 21, "fkaveinga@gmail.com");
when(userService.getById(1)).thenReturn(mockUser);
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/users/1").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is("folau")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.age", is(21)));
}
@Test
public void testGetAllUsers() throws Exception {
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("folaulau", 21, "folaulau@gmail.com"), new User("kinga", 21, "kinga@gmail.com"));
when(userService.getAll()).thenReturn(users);
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/users").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$[0].firstName", is("folaulau")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$[0].age", is(21)));
}
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() throws Exception {
User user = new User("kinga", "kaveinga", 21, "kinga@gmail.com");
User savedUser = new User(1, "kinga", "kaveinga", 21, "kinga@gmail.com");
when(userService.update(user)).thenReturn(savedUser);
this.mockMvc.perform(patch("/users/update").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(user.toJson()))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is("kinga")))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.id", is(1)));
}
@Test
public void testRemoveUser() throws Exception {
long id = 1;
when(userService.remove(id)).thenReturn(true);
this.mockMvc.perform(delete("/users/" + id)).andDo(print()).andExpect(status().isOk()).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("true"));
}
}
Unit Testing business logic with Mockito
- Mock objects with the when() method
- Verify that methods are called correctly within the logic you are testing. Use the verify() method.
- Use AssertThat utility methods to check expected test result.
@Test
public void testSignUp() throws Exception {
log.info("testSignUp()");
User user = ConstantUtils.generateUser();
when(userDAO.save(any(User.class))).thenReturn(user);
when(userNtcService.sendWelcomeEmail(any(User.class))).thenReturn(true);
User signedUpUser = userService.signUp(user);
InOrder inOrder = Mockito.inOrder(userDAO, userNtcService);
inOrder.verify(userDAO, times(1)).save(userCaptor.capture());
assertEquals(user, signedUpUser);
log.info("user captor email={}", userCaptor.getValue().getEmail());
assertThat(userCaptor.getValue()).isSameAs(signedUpUser);
log.info("testSignUp() - passed\n\n");
}
Testing DAO(Database Access Object)
- Use @Transactional so that database changes will be rolled back.
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@DataJpaTest
public class UserRepositoryTest {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
List<User> testUsers = new ArrayList<User>();
@Before
public void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
User user = ConstantUtils.generateUser();
user = userRepository.saveAndFlush(user);
testUsers.add(user);
// log.info("user={}",ObjectUtils.toJson(user));
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void testSaveUser() {
User user = ConstantUtils.generateUser();
log.info("user={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(user));
User savedUser = userRepository.saveAndFlush(user);
log.info("savedUser={}", ObjectUtils.toJson(savedUser));
assertNotNull(savedUser);
log.info("savedUser==user -> {}", savedUser == user);
assertEquals(user, savedUser);
long count = userRepository.count();
log.info("count={}", count);
assertEquals(8, count);
log.info("\n\ntestSave passed\n");
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void testFindByName() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
log.info("testFindByName({})", testUsers.get(0).getFirstName());
String lastName = testUsers.get(0).getLastName();
List<User> savedUsers = userRepository.findByLastName(lastName);
log.info(savedUsers.toString());
assertNotNull(savedUsers);
assertNotEquals(savedUsers.size(), 0);
log.info("\n\ntestFindByName passed\n");
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void testFindByEmail() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
log.info("testFindByEmail({})", testUsers.get(0).getEmail());
User savedUser = userRepository.findByEmail(testUsers.get(0).getEmail());
assertNotNull(savedUser);
assertNotEquals(savedUser.getId().longValue(), 0);
System.out.println(savedUser.toString());
log.info("\n\ntestFindByEmail passed\n");
}
}
Spy
Spy is a wrapper which is used to override method(s) and return value(s) and ignore logic with those methods.
- Use @Spy on the service to spy or Mockito.spy() method.
- Use lenient().doReturn(returnedValue).when(service).method();
@Spy
private UserService spyUserService = new UserServiceImp();
@Test
public void test_SignUpWithPlanAndSpy() throws Exception {
log.info("test_SignUpWithPlanAndSpy()");
User user = null;
double planAmount = 200.0;
Plan plan = new Plan(1L, planAmount, user);
planAmount = 500.0;
Plan savedPlan = new Plan(1L, planAmount, user);
// This call is not actually made. Execution flow does not get within the signUpForPlan(check the log within the
// method)
lenient().doReturn(savedPlan).when(spyUserService).signUpForPlan(plan);
assertThat(savedPlan.getAmount()).isEqualTo(planAmount);
log.info("test_SignUpWithPlanAndSpy() - passed!");
}