AWS – CodePipeline
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous delivery service that helps you automate your release pipelines for fast and reliable application and infrastructure updates. CodePipeline automates the build, test, and deploy phases of your release process every time there is a code change, based on the release model you define. This enables you to rapidly and reliably deliver features and updates. You can easily integrate AWS CodePipeline with third-party services such as GitHub or with your own custom plugin. With AWS CodePipeline, you only pay for what you use. There are no upfront fees or long-term commitments.
Benefits
Rapid delivery – AWS CodePipeline automates your software release process, allowing you to rapidly release new features to your users. With CodePipeline, you can quickly iterate on feedback and get new features to your users faster.
Easy to integrate – AWS CodePipeline can easily be extended to adapt to your specific needs. You can use our pre-built plugins or your own custom plugins in any step of your release process. For example, you can pull your source code from GitHub, use your on-premises Jenkins build server, run load tests using a third-party service, or pass on deployment information to your custom operations dashboard.
How it works:

Set up
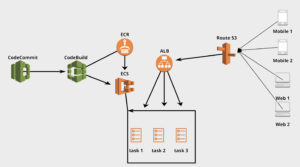
Codecommit
Code repository for you source code.
Codebuild
Codebuild will build and and deploy new code to a specified destination. Make sure that your codebuild role is able to perform actions on other aws services when your code is being built. For example you might want to push your build to S3 or ECR. In this case, you will have to add policy to your role to perform that.
buildSpec.yml file specifies how you want to build your code. It must be in the root folder of you project.
ECR
ECR stores docker images built by codebuild. These docker images have the latest code built in codebuild can can be deployed into ECS.
ECS
ECS has task definitions where you define what kind of services you might want to run.
Task Definition defines the following:
- Type of server to use(ec2 or fargate)
- VPC where the server where live
- Memory and CPU allocated to the server
- Port number of the server
- ECR image to deployed on the server
- Entrypoint endpoint that starts your server(java,-jar,-Dspring.profiles.active=dev,app.jar)
- Environment variables to pass into the server/container (spring.profiles.active=dev). You can store database credentials here which is better than storing in property files
- Cloudwatch log group for logging
Service defines the following:
- Number of servers to run
- Load balancer(ALB) to listen to
- Target Group
- Health check for servers
- Type of deployment(Rolling Update and Blue/Green)
- Security Group to use for the server
Note: Security group must enable ports where the server will listen to as well as the target group listens to. For example target group checks server health on port 80 and spring boot server listens on port 8080. Now in the security group, enable 80 and 8080 from anywhere.
ALB
Application load balancer handles requests and loads balance them to your tasks(servers). Load balancer has rules you can use for redirect or forward depending on path. This is also where you add certificate to your server. ALB can be configured to forward certain requests based on the url path to specific destination.
Route 53
Route 53 routes traffic to our ALB.
aws codepipeline list-pipelines
aws codepipeline get-pipeline-state --name MyFirstPipeline
Start the execution of a pipeline
aws codepipeline start-pipeline-execution --name MyFirstPipeline
Stop the execution of a pipeline
aws stop-pipeline-execution --pipeline-name MyFirstPipeline --pipeline-execution-id yes98sd00890
Build springboot project with Codebuild and deploy it to ECS
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/latest/userguide/ecs-cd-pipeline.html
Continuous Integration Best Practices 2018
AWS – CodeDeploy
August 5, 2019AWS – Codecommit
AWS CodeCommit is a fully-managed source control service that hosts secure Git-based repositories. It makes it easy for teams to collaborate on code in a secure and highly scalable ecosystem. CodeCommit eliminates the need to operate your own source control system or worry about scaling its infrastructure. You can use CodeCommit to securely store anything from source code to binaries, and it works seamlessly with your existing Git tools.
AWS CodeCommit eliminates the need to host, maintain, back up, and scale your own source control servers. The service automatically scales to meet the growing needs of your project.
AWS CodeCommit helps you collaborate on code with teammates via pull requests, branching, and merging. You can implement workflows that include code reviews and feedback by default, and control who can make changes to specific branches.
AWS CodeCommit supports all Git commands and works with your existing Git tools. You can keep using your preferred development environment plugins, continuous integration/continuous delivery systems, and graphical clients with CodeCommit.
AWS CodeCommit automatically encrypts your files in transit and at rest. CodeCommit is integrated with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allowing you to customize user-specific access to your repositories.
Set up permission for codecommit
AWS Codecommit Developer Guide
August 5, 2019AWS – Kinesis
August 5, 2019AWS – ElasticBeanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an easy-to-use service for deploying and scaling web applications and services developed with Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker on familiar servers such as Apache, Nginx, Passenger, and IIS.
You can simply upload your code and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling to application health monitoring. At the same time, you retain full control over the AWS resources powering your application and can access the underlying resources at any time.
There is no additional charge for Elastic Beanstalk – you pay only for the AWS resources needed to store and run your applications.
Elastic Beanstalk automatically scales your application up and down based on your application’s specific need using easily adjustable Auto Scaling settings. For example, you can use CPU utilization metrics to trigger Auto Scaling actions. With Elastic Beanstalk, your application can handle peaks in workload or traffic while minimizing your costs.
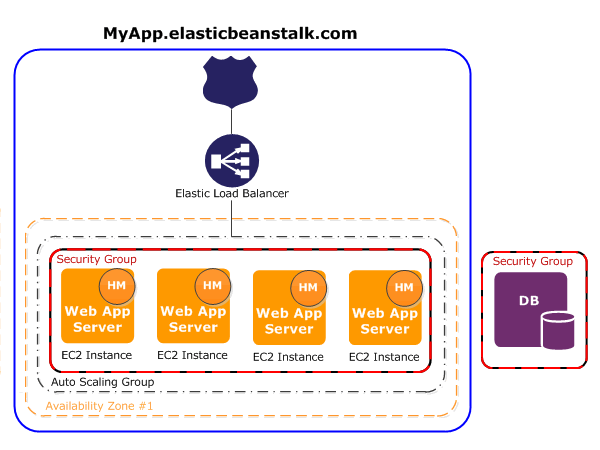
AWS Elastic Beanstalk Developer Guide
August 5, 2019