Git clone
The git clone command is used to clone or copy a remote repository onto a destination such as your laptop or a remote server.
Git supports ssh and https network protocols.
Git clone ssh
git clone ssh://folauk@gmail.com/path/to/my-project.git // example git clone ssh://git@github.com:folaulau/spring-data.git
Git clone https
git clone http[s]://host.xz[:port]/path/to/repo.git // example git clone https://github.com/folaulau/spring-data.gitApril 5, 2019
Git set up
The git init command is used to create a git repository. The git init creates a .git subdirectory which contains the git metadata for the repository. Keep in mind that the current directory in which you run the git init command will be the repository.
// make the current direct a repository git init
// create a new repository in a new directory git init directory-name // example git init test-repo
If your run git init again in a repository it will not overide the existing configurations.
How to create a new local repository and push it to remote
- git init my-repo
- cd my-repo
- add something to my-repo
- git remote add origin https://github.com/repo-location.git
- git add .
- git commit -m “First commit”
- git push origin master
*** All though this works, it is better to create a remote repository and then clone it to your computer or server.
April 5, 2019MySQL Sub Query
A sub query is a query within a query. A subquery can take place in a SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clause. A subquery can be used in a INSERT, UPDATE, SELECT, and DELETE query.
The main query is called the outer query and the subquery in called the inner query.
The sub query is executed and its results are passed to the outer query which is then executed after.
SELECT
column_name1, column_name2,....
FROM
table_name1
WHERE
column_name1 operator (SELECT
column_name
FROM
table_name2
);
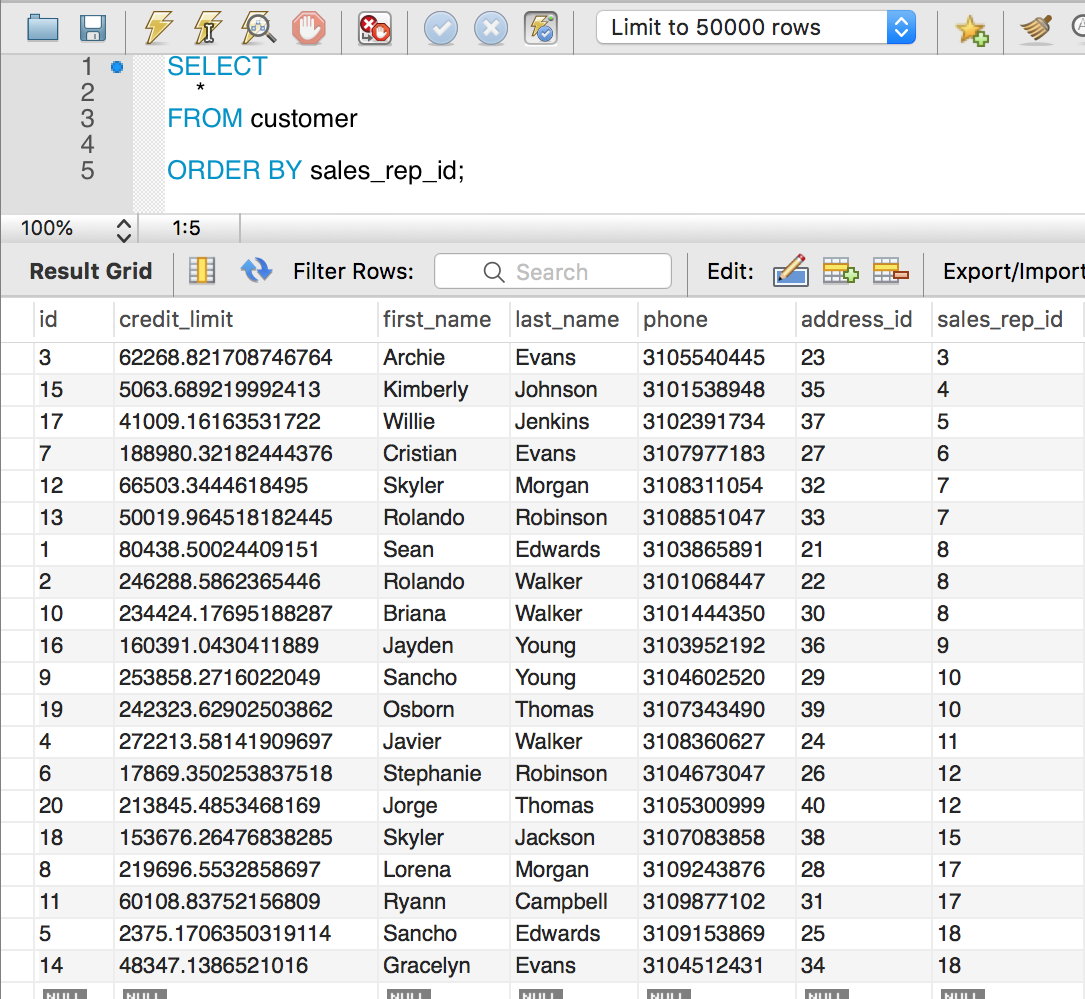
Here we are filter out rows with sales_rep_id that is less than the three smallest sales_rep_id which is, in this case, 3, 4, and 5.
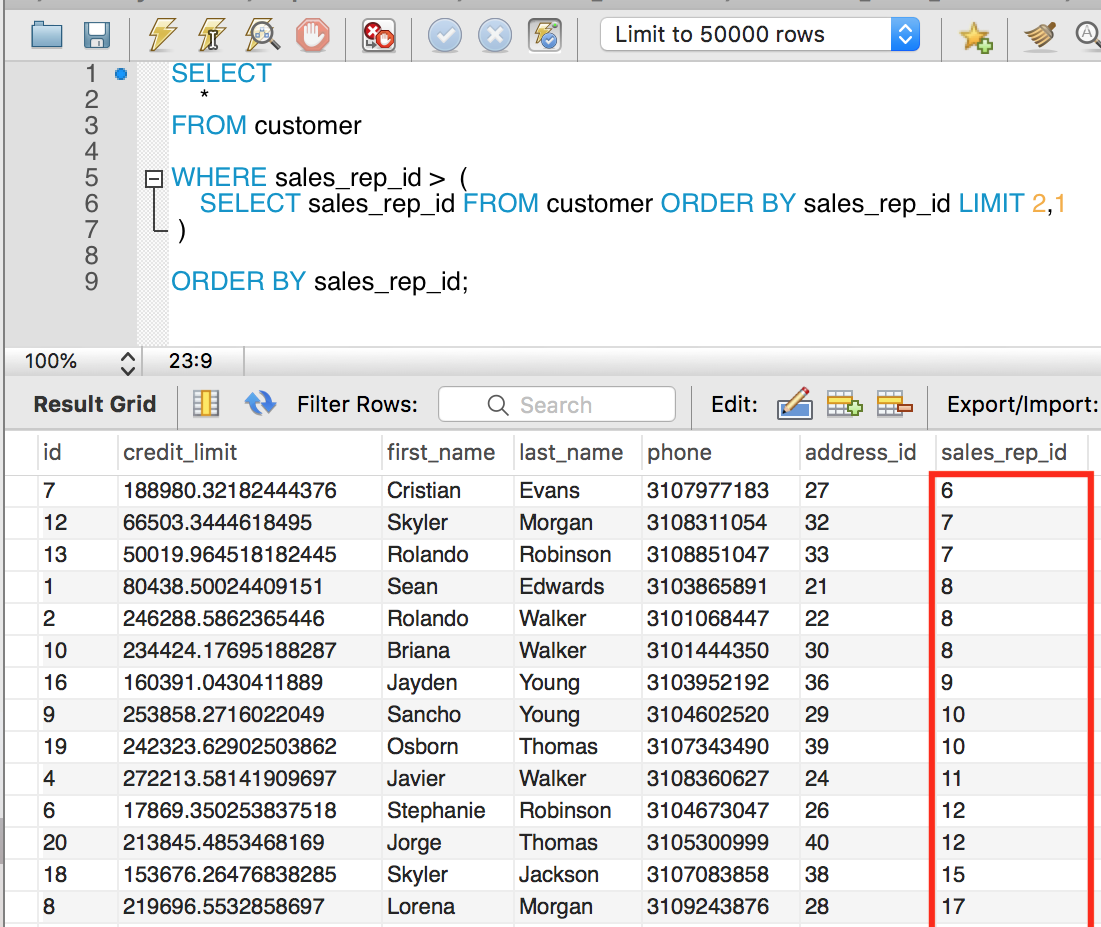
Subquery in FROM clause
Subquery in the FROM clause forms a derived or temporary table. This derived or temporary table must have an alias.
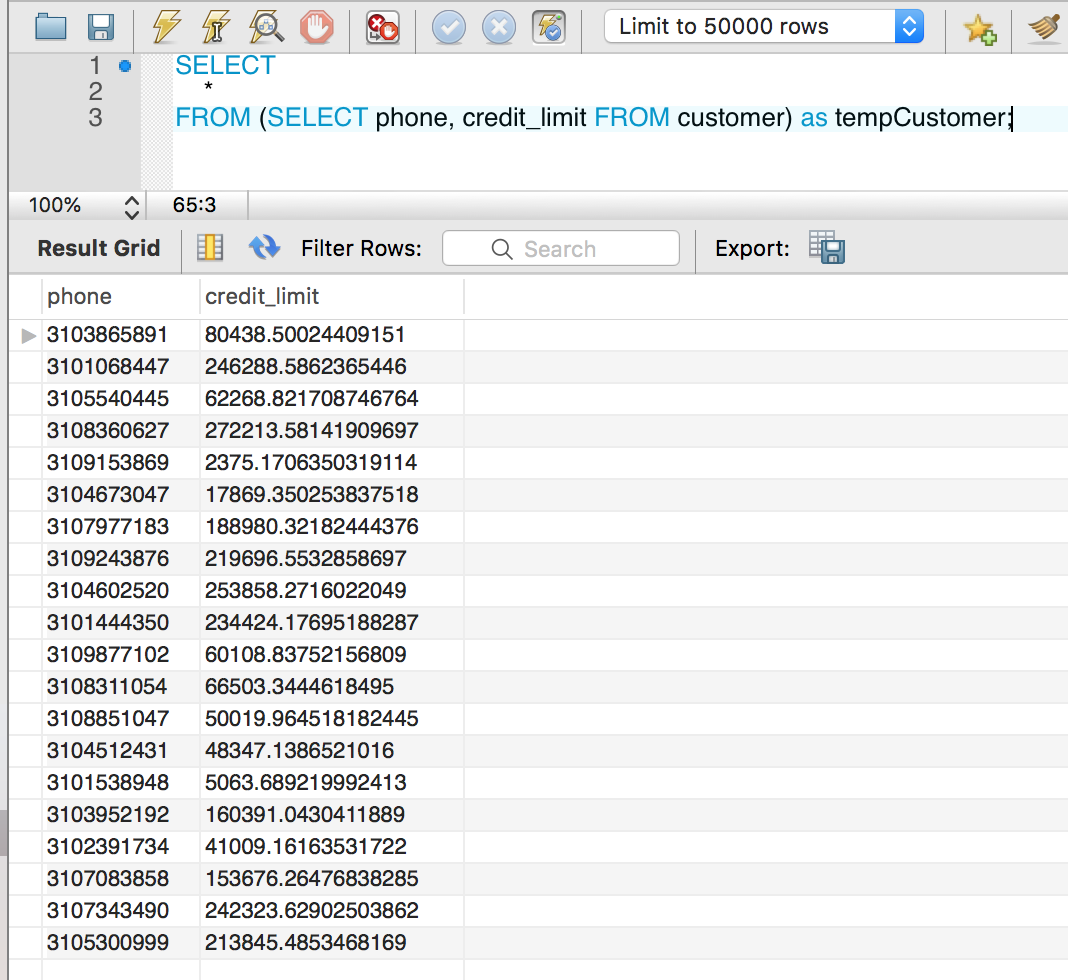
As you can see, “(SELECT phone, credit_limit FROM customer) as tempCustomer” formed a derived table.
Correlated subquery
A correlated subquery is different from a regular subquery that stands alone. A correlated subquery uses columns or data from the outer query. It evaluates once for every row in the outer query.
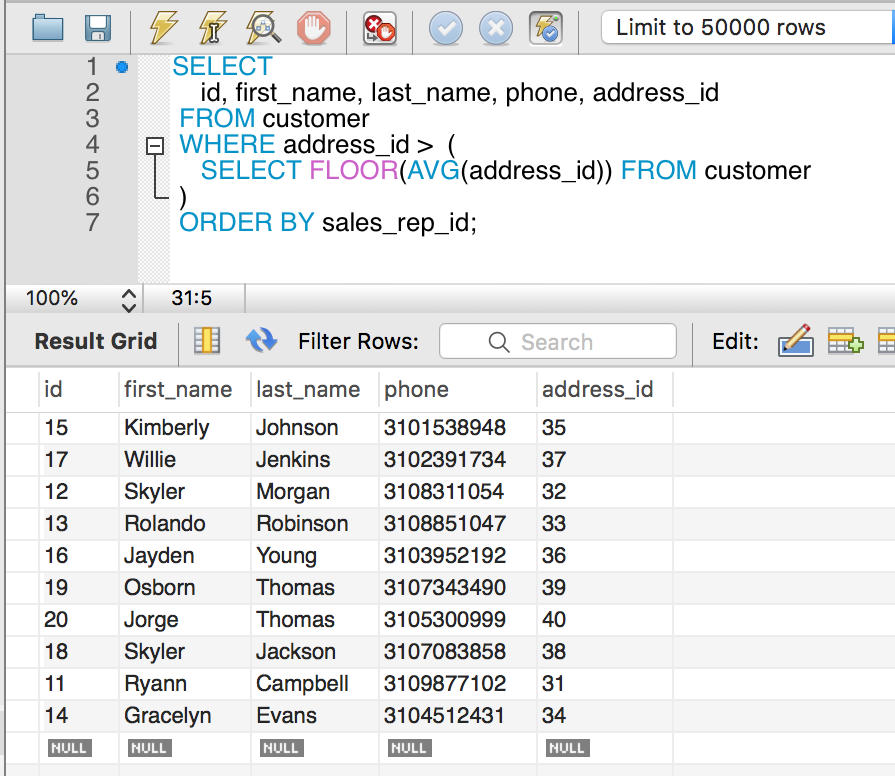
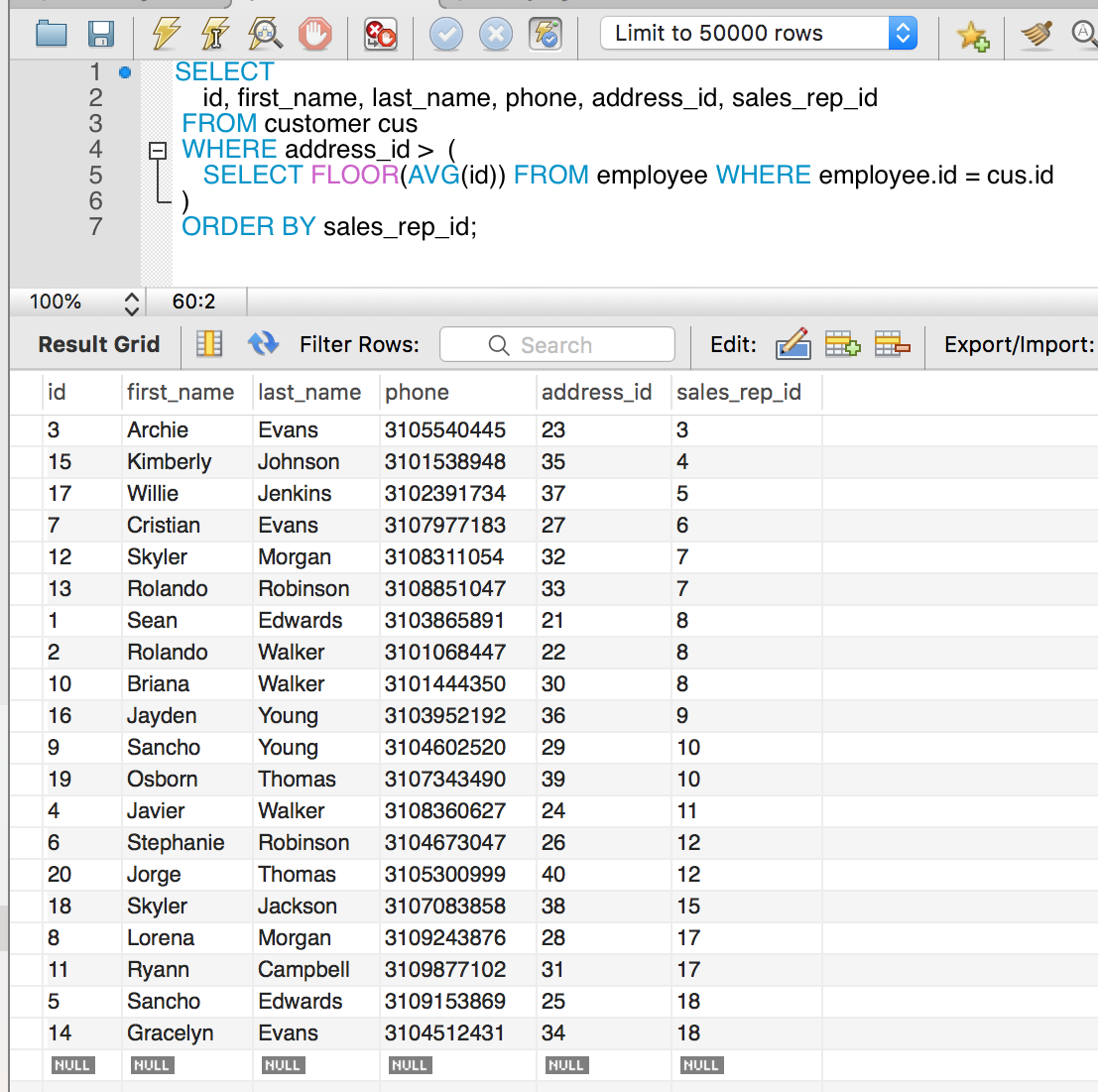
Here is another example where we select all customers with address id that is greater than the average id of the employee.
MySQL Self Join
Self Join is designed to return rows with other rows within the same table. Table1 is joined with itself.
SELECT column_name1,column_name2,... FROM table_name1 tab1, INNER JOIN table_name1 tab2 ON condition;
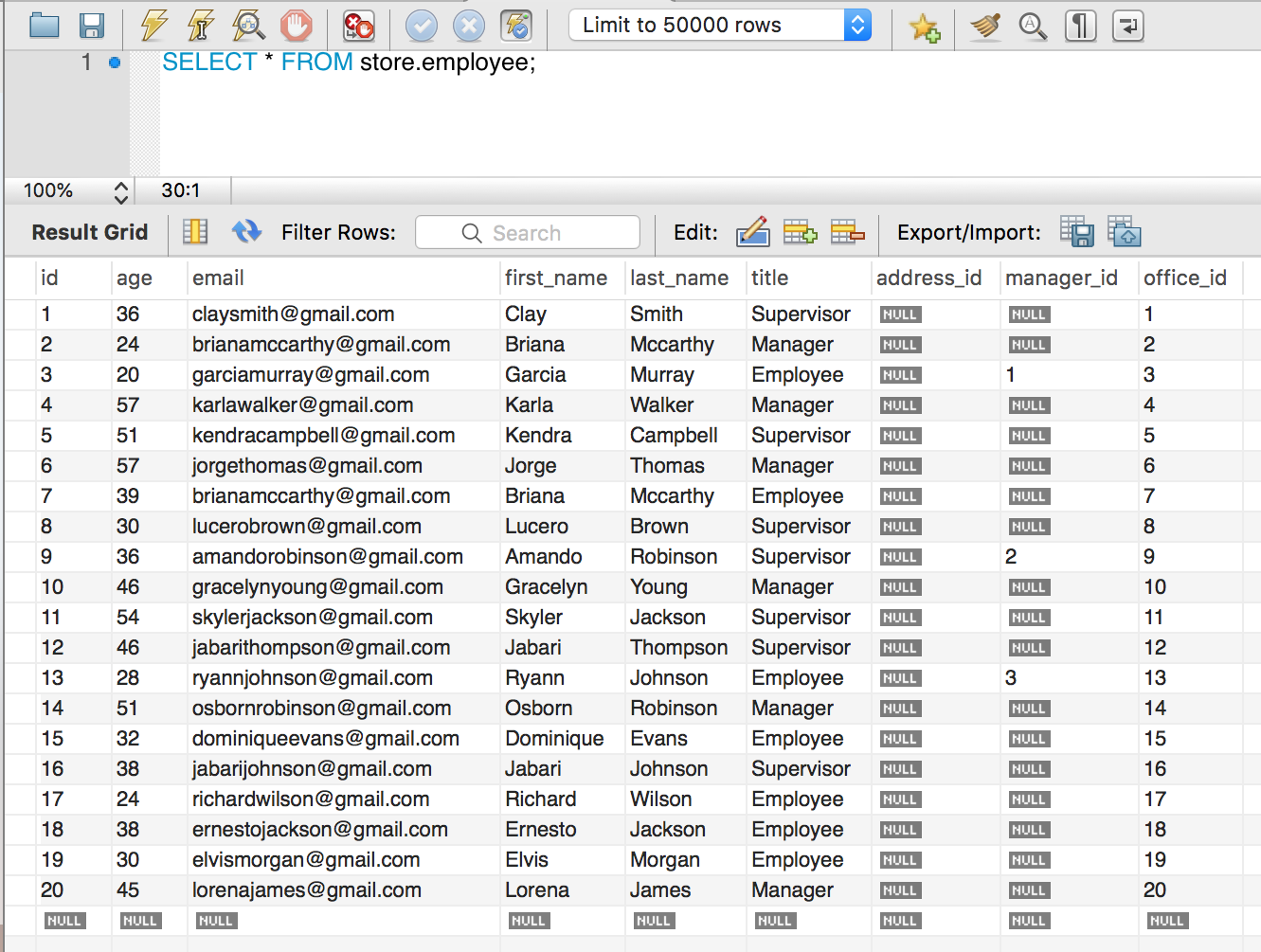
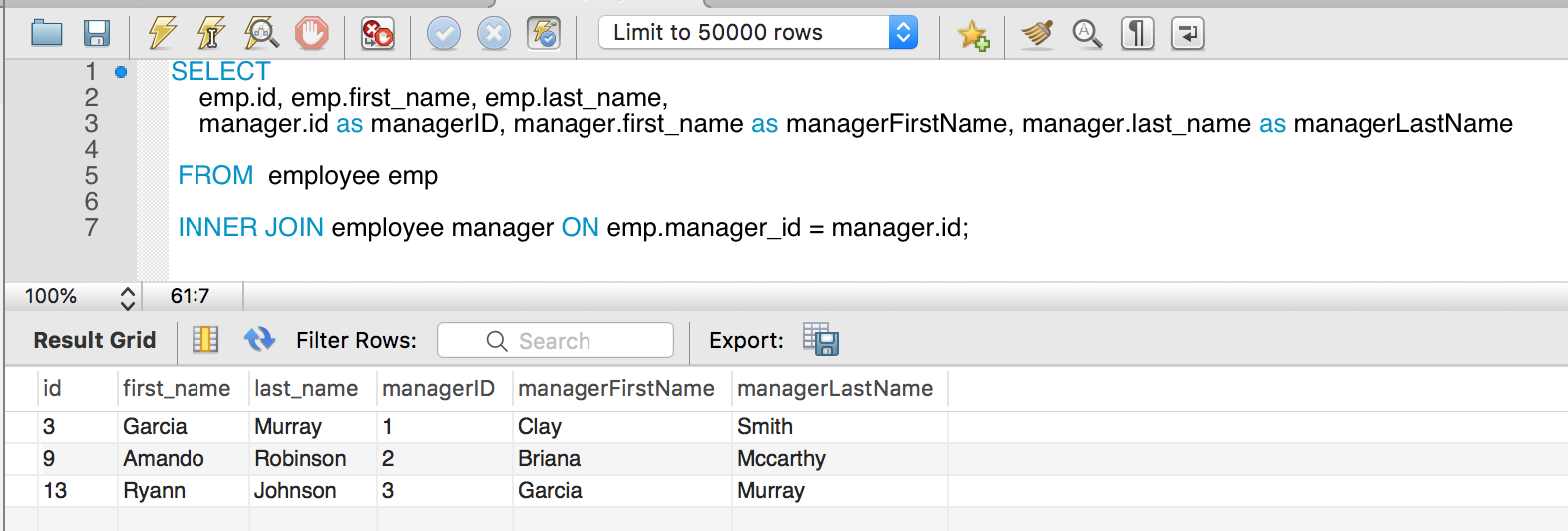
We are joining employees to their managers. You must use ALIAS for the table to distinguish the difference.
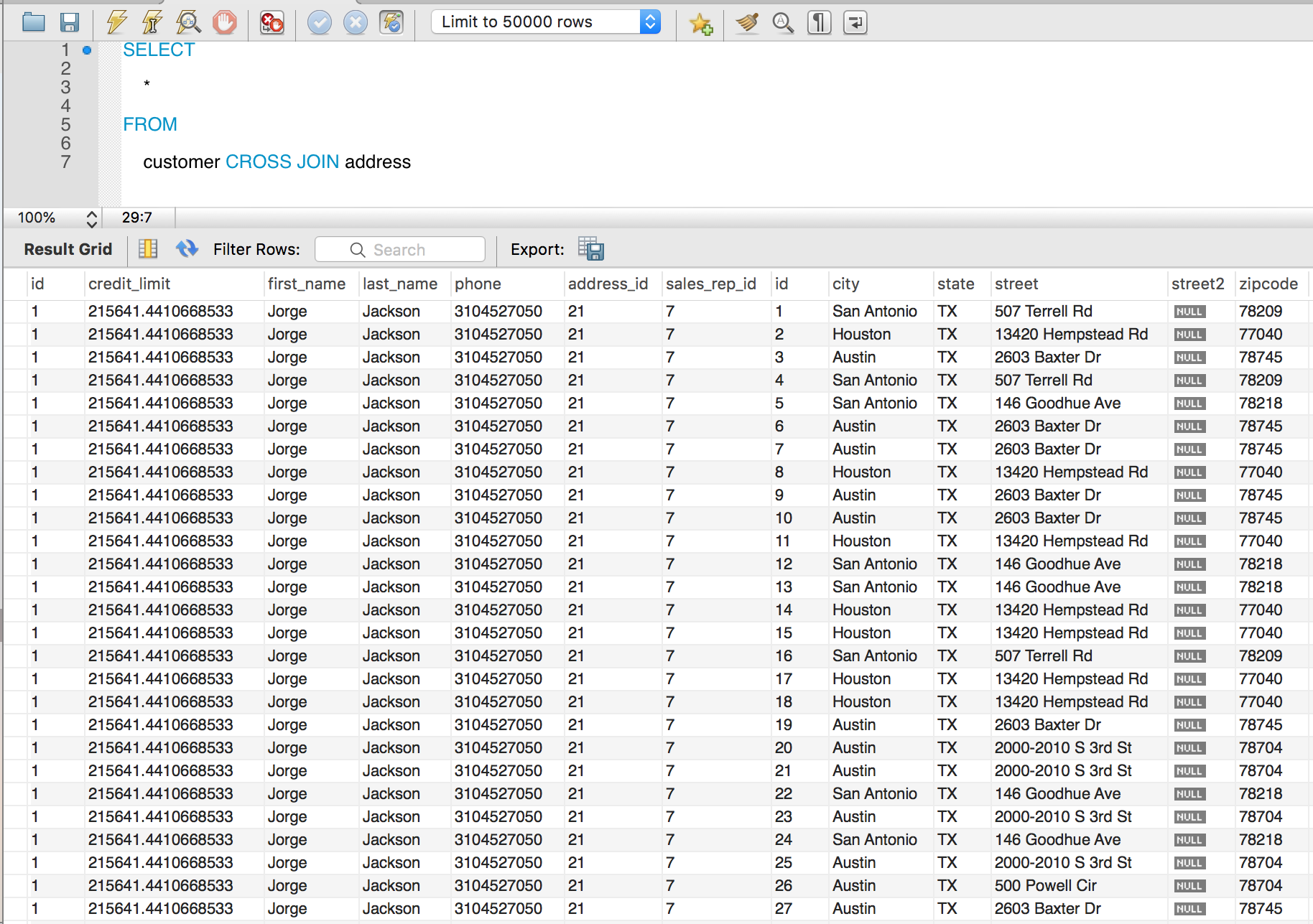
MySQL Cross Join
The CROSS JOIN is used to join all rows from one table to all rows of another table.
SELECT
*
FROM
table_name1
CROSS JOIN
table_name2;