HTML Introduction
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. It is the most widely used language on the web. A markup language uses sets of markup tags to characterize text elements within a document, which gives instructions to the web browsers on how the document should appear.
Originally, HTML was developed with the intent of defining the structure of documents like headings, paragraphs, lists, and so forth to facilitate the sharing of scientific information between researchers. Now, HTML is being widely used to format web pages with the help of different tags available in HTML language.
HTML is a MUST for students and working professionals to become a great Software Engineer specially when they are working in Web Development Domain. Here are the reasons why you should learn HTML:
- Create a Web site – You can create a website or customize an existing web template if you know HTML well.
- Become a web designer / developer– If you want to start a carrer as a professional web designer, HTML and CSS designing is a must skill. If you want to optimize your website, to boost its speed and performance, it is good to know HTML to yield best results.
- Learn other languages – HTML helps you understand other languages such as javascript, php, java once you have its basics down.
Testing
Resources
https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/testing/
Visual Studio Code Hot Keys
Search
Search for file in your space
Windows
CTRL + P
Mac
command + P
HTML SEO
Title
Description
Social Media Tags
Viewport metadata
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/>
MySQL Event
MySQL Events or scheduled events are tasks that execute according to a specified schedule. They are stored in the database and executed at one or more intervals.
For example, you can create an event that optimizes a table by backfilling data from another table the database that runs at 1:00 AM every day.
MySQL Events are also known as “temporal triggers” because they are triggered by time, not by DML events like normal triggers. MySQL events are similar to a cronjob on Linux or a task scheduler on Windows. MySQL Event Scheduler manages the schedule and execution of Events. MySQL Events can be very useful in many cases such as optimizing database tables, cleaning up logs, archiving data, or generating complex reports during off-peak time.
Run SHOW PROCESSLIST to make sure that event_scheduler User shows up as an indication that you can create an event.
SHOW PROCESSLIST;
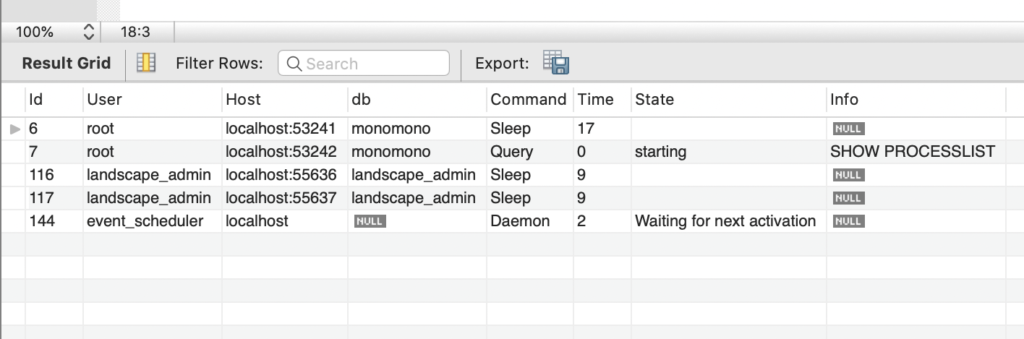
Show event details
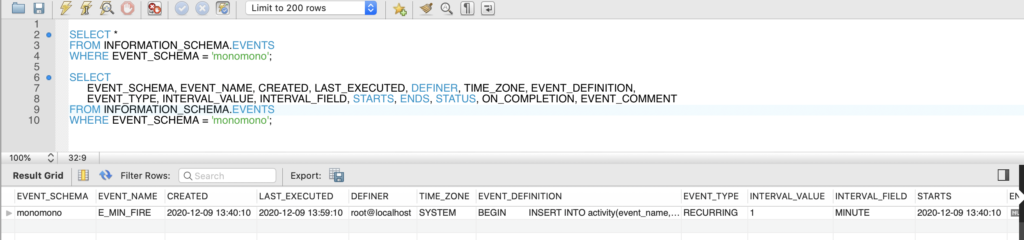
You can use show events query to show details of events. You can also use the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.EVENTS table to do the same.
SELECT *
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.EVENTS
WHERE EVENT_SCHEMA = 'database_name';
SELECT
EVENT_SCHEMA, EVENT_NAME, CREATED, LAST_EXECUTED, DEFINER, TIME_ZONE, EVENT_DEFINITION,
EVENT_TYPE, INTERVAL_VALUE, INTERVAL_FIELD, STARTS, ENDS, STATUS, ON_COMPLETION, EVENT_COMMENT
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.EVENTS
WHERE EVENT_SCHEMA = 'database_name';
SHOW EVENTS FROM database_name;
Turn on and off the event scheduler
-- turn on event_scheduler SET GLOBAL event_scheduler = ON; -- turn off event_scheduler SET GLOBAL event_scheduler = OFF;
CREATE EVENT requires the EVENT privilege for the schema in which the event is to be created. If the DEFINER clause is present, the privileges required depend on the user value. An event is associated with a schema. If no schema is indicated as part of event_name, the default (current) schema is assumed.
// This event executes once—one hour following its creation
CREATE EVENT myevent
ON SCHEDULE AT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
DO
UPDATE myschema.sometable SET somecol = somecol + 1;
Recurring event with end time
With ENDS the recurring event will stop its execution at that time.
CREATE EVENT IF NOT EXISTS E_MAX_FIRE
ON
SCHEDULE EVERY 1 MINUTE
STARTS CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
ENDS CURRENT_TIMESTAMP + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
DO
INSERT INTO activity(event_name, event_fired_at)
VALUES('max-event',NOW());
Recurring event with stored procedure
Note that with no ENDS clause the recurring event will continue to execute at EVERY 1 MINUTE forever.
delimiter |
CREATE EVENT E_MIN_FIRE
ON SCHEDULE
EVERY 1 MINUTE
STARTS CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
COMMENT 'Saves total number of sessions then clears the table each day'
DO
BEGIN
INSERT INTO activity(event_name, event_fired_at)
VALUES('min-event',NOW());
END |
delimiter ;
DROP EVENT [IF EXISTS] event_name; // delete E_MIN_FIRE event DROP EVENT IF EXISTS E_MIN_FIRE;