AWS – S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. This means customers of all sizes and industries can use it to store and protect any amount of data for a range of use cases, such as websites, mobile applications, backup and restore, archive, enterprise applications, IoT devices, and big data analytics. Amazon S3 provides easy-to-use management features so you can organize your data and configure finely-tuned access controls to meet your specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements. Amazon S3 is designed for 99.999999999% (11 9’s) of durability, and stores data for millions of applications for companies all around the world.
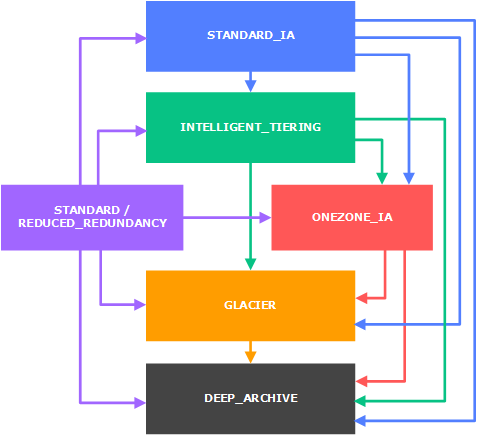
Use cases:
- Backup and restore
- Disaster recovery
- Archive
- Data lakes and big data analytics
- Hybrid cloud storage
- Cloud-native application data
Overview of S3
Amazon S3 has a simple web services interface that you can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web.
S3 Bucket
S3 Bucket Restrictions and Limitations
- By default, you can create up to 100 buckets per account. You can go more than 100 buckets per account by submitting a support ticket. You can increase your account bucket limit to a maximum of 1,000 buckets.
- Bucket ownership is not transferable; however, if a bucket is empty, you can delete it. After a bucket is deleted, the name becomes available to reuse, but the name might not be available for you to reuse for various reasons. For example, some other account could create a bucket with that name. Note, too, that it might take some time before the name can be reused. So if you want to use the same bucket name, don’t delete the bucket.
- There is no limit to the number of objects that can be stored in a bucket and no difference in performance whether you use many buckets or just a few. You can store all of your objects in a single bucket, or you can organize them across several buckets.
- After you have created a bucket, you can’t change its Region.
- You cannot create a bucket within another bucket.
- If your application automatically creates buckets, choose a bucket naming scheme that is unlikely to cause naming conflicts. Ensure that your application logic will choose a different bucket name if a bucket name is already taken.
- After you create an S3 bucket, you can’t change the bucket name, so choose the name wisely.
Rules for bucket naming
- Bucket names must be unique across all existing bucket names in Amazon S3.
- Bucket names must comply with DNS naming conventions.
- Bucket names must be at least 3 and no more than 63 characters long.
- Bucket names must not contain uppercase characters or underscores.
- Bucket names must start with a lowercase letter or number.
- Bucket names must not be formatted as an IP address (for example, 192.168.5.4).
When you use server-side encryption, Amazon S3 encrypts an object before saving it to disk in its data centers and decrypts it when you download the objects.
- Key – The name that you assign to an object. You use the object key to retrieve the object.
- Version Id – Within a bucket, a key and version ID uniquely identify an object. The version ID is a string that Amazon S3 generates when you add an object to a bucket.
- Value – The content that you are storing. An object value can be any sequence of bytes. Objects can range in size from zero to 5 TB.
- Metadata – A set of name-value pairs with which you can store information regarding the object. You can assign metadata, referred to as user-defined metadata, to your objects in Amazon S3. Amazon S3 also assigns system-metadata to these objects, which it uses for managing objects.
- Subresources – Amazon S3 uses the subresource mechanism to store object-specific additional information.
- Access Control Information – You can control access to the objects you store in Amazon S3. Amazon S3 supports both the resource-based access control, such as an access control list (ACL) and bucket policies and user-based access control. Because subresources are subordinates to objects, they are always associated with some other entity such as an object or a bucket
Object key (or key name) uniquely identifies the object in a bucket. Object metadata is a set of name-value pairs. You can set object metadata at the time you upload it. After you upload the object, you cannot modify object metadata. The only way to modify object metadata is to make a copy of the object and set the metadata.
The Amazon S3 data model is a flat structure: you create a bucket, and the bucket stores objects. There is no hierarchy of sub buckets or subfolders. However, you can infer logical hierarchy using key name prefixes and delimiters as the Amazon S3 console does. The Amazon S3 console supports a concept of folders.
Amazon S3 supports buckets and objects, and there is no hierarchy in Amazon S3. However, the prefixes and delimiters in an object key name enable the Amazon S3 console and the AWS SDKs to infer hierarchy and introduce the concept of folders.
System Metadata – For each object stored in a bucket, Amazon S3 maintains a set of system metadata. Amazon S3 processes this system metadata as needed. For example, Amazon S3 maintains object creation date and size metadata and uses this information as part of object management.
User-defined Metadata – When uploading an object, you can also assign metadata to the object.
AmazonS3 s3Client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withCredentials(new ProfileCredentialsProvider())
.withRegion(clientRegion)
.build();
if (!s3Client.doesBucketExistV2(bucketName)) {
// Because the CreateBucketRequest object doesn't specify a region, the
// bucket is created in the region specified in the client.
s3Client.createBucket(new CreateBucketRequest(bucketName));
// Verify that the bucket was created by retrieving it and checking its location.
String bucketLocation = s3Client.getBucketLocation(new GetBucketLocationRequest(bucketName));
System.out.println("Bucket location: " + bucketLocation);
}
AmazonS3 s3Client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(clientRegion)
.build();
// Upload a text string as a new object.
s3Client.putObject(bucketName, stringObjKeyName, "Uploaded String Object");
// Upload a file as a new object with ContentType and title specified.
PutObjectRequest request = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, fileObjKeyName, new File(fileName));
ObjectMetadata metadata = new ObjectMetadata();
metadata.setContentType("plain/text");
metadata.addUserMetadata("x-amz-meta-title", "someTitle");
request.setMetadata(metadata);
s3Client.putObject(request);
You need to santize your key names because they must be presentable as urls. Read here about that.
So I have a method to strip out invalid characters from file name because creating a key off of it.
public static String replaceInvalidCharacters(String fileName) {
/**
* Valid characters<br>
* alphabets a-z <br>
* digits 0-9 <br>
* underscore _ <br>
* dash - <br>
*
*/
String alphaAndDigits = "[^a-zA-Z0-9._-]+";
// remove invalid characters
String newFileName = fileName.replaceAll(alphaAndDigits, "");
return newFileName;
}
AmazonS3 s3Client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(clientRegion)
.withCredentials(new ProfileCredentialsProvider())
.build();
// Get an object and print its contents.
System.out.println("Downloading an object");
fullObject = s3Client.getObject(new GetObjectRequest(bucketName, key));
System.out.println("Content-Type: " + fullObject.getObjectMetadata().getContentType());
System.out.println("Content: ");
displayTextInputStream(fullObject.getObjectContent());
// Get a range of bytes from an object and print the bytes.
GetObjectRequest rangeObjectRequest = new GetObjectRequest(bucketName, key)
.withRange(0, 9);
objectPortion = s3Client.getObject(rangeObjectRequest);
System.out.println("Printing bytes retrieved.");
displayTextInputStream(objectPortion.getObjectContent());
// Get an entire object, overriding the specified response headers, and print the object's content.
ResponseHeaderOverrides headerOverrides = new ResponseHeaderOverrides()
.withCacheControl("No-cache")
.withContentDisposition("attachment; filename=example.txt");
GetObjectRequest getObjectRequestHeaderOverride = new GetObjectRequest(bucketName, key)
.withResponseHeaders(headerOverrides);
headerOverrideObject = s3Client.getObject(getObjectRequestHeaderOverride);
displayTextInputStream(headerOverrideObject.getObjectContent());
AmazonS3 s3Client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(clientRegion)
.withCredentials(new ProfileCredentialsProvider())
.build();
// Set the presigned URL to expire after one hour.
java.util.Date expiration = new java.util.Date();
long expTimeMillis = expiration.getTime();
expTimeMillis += 1000 * 60 * 60;
expiration.setTime(expTimeMillis);
// Generate the presigned URL.
System.out.println("Generating pre-signed URL.");
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest generatePresignedUrlRequest =
new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, objectKey)
.withMethod(HttpMethod.GET)
.withExpiration(expiration);
URL url = s3Client.generatePresignedUrl(generatePresignedUrlRequest);
System.out.println("Pre-Signed URL: " + url.toString());
AmazonS3 s3Client = AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(clientRegion)
.withCredentials(new ProfileCredentialsProvider())
.build();
// Set the presigned URL to expire after one hour.
java.util.Date expiration = new java.util.Date();
long expTimeMillis = expiration.getTime();
expTimeMillis += 1000 * 60 * 60;
expiration.setTime(expTimeMillis);
// Generate the presigned URL.
System.out.println("Generating pre-signed URL.");
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest generatePresignedUrlRequest =
new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, objectKey)
.withMethod(HttpMethod.GET)
.withExpiration(expiration);
URL url = s3Client.generatePresignedUrl(generatePresignedUrlRequest);
System.out.println("Pre-Signed URL: " + url.toString());
How to create a S3 bucket from AWS CLI
aws s3 mb s3://mybucket
aws s3 cp test.txt s3://mybucket/test2.txt --expires 2014-10-01T20:30:00Z
aws s3 mv test.txt s3://mybucket/test2.txt // upload all contents within the current directory to mybucket aws s3 mv . s3://mybucket
Download files from a S3 bucket
aws s3 mv s3://mybucket/test.txt test2.txt //download all files in mybucket to a local director(local_mybucket) aws s3 mv s3://mybucket local_mybucket --recursive
Sync files
// sync(upload all files) within the current directory to S3 mybucket aws s3 sync s3://mybucket . // sync mybucket to mybucket2 aws s3 sync s3://mybucket s3://mybucket2 // download all content of mybucket to the current directory aws s3 sync s3://mybucket . --recursive //any files existing in the local directory but not existing in bucket will be deleted. aws s3 sync . s3://mybucket --delete // all files matching the pattern existing both in s3 and locally will be excluded from the sync. aws s3 sync . s3://mybucket --exclude "*.jpg"
List s3 buckets within your account
aws s3api list-buckets //The query option filters the output of list-buckets down to only the bucket names. aws s3api list-buckets --query "Buckets[].Name"
aws s3api list-objects --bucket bucketName // get objects that start with (--prefix) aws s3api list-objects --bucket sidecarhealth-dev-file-form --prefix prefixValue