MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID
The MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the most recently generated integer successfully inserted for an AUTO_INCREMENT column.
CREATE TABLE user(
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL
...,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
If you insert multiple rows into the table using a single INSERT statement, the LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the first automatically generated value only.
If the insertion fails, the result returned by the LAST_INSERT_ID() remain unchanged.
The LAST_INSERT_ID() function works based on client-independent(database connection) principle. It means the value returned by the LAST_INSERT_ID() function for a specific client is the value generated by that client only to ensure that each client can obtain its own unique ID. This means that each database connection will have its own LAST_INSERT_ID().
INSERT INTO user(name)
VALUES('Folau');
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
The result is 1 which is the first id in the table.
MySQL Transaction
June 12, 2019Git restore deleted commit
Sometime you commit something but then accidentally deleted it and then you would like to bring it back or continue working on it. I had this happened to me and it was frustrating to redo everything I deleted. But then I found out there is a way to recover deleted commit.
Well, you want to reset to that commit so you can continue working on it. Using git reflog, which will show you logs on what you have committed, will show you your deleted commit hash which then you can use to reset to.
git reflog
git reset –hard f52ee7b
June 7, 2019Git reset
Get list of commits to choose from
git log
Git reset can change the branch pointer to point to any commit in the tree.
git reset --hard <hash>
$ git reset --hard 07a2a46
HEAD is now at 07a2a46 Updated index.html
If you quickly check the log, you will see no history of the commits after 07a2a46
Update branch on remote
git push or git push origin HEAD --force
Spring Boot Code Structure
It is very important to structure your code in a way that is maintainable and easy to work with. A lot of times developers drag their feet to work on a project that is unorganized and hard to follow. Your team members will appreciate the fact that you took the time to organize your code to a certain structure. There are mainly two ways to organize your code. One is by component or layer and the other is by entities.
Component or Layer Driven Layout
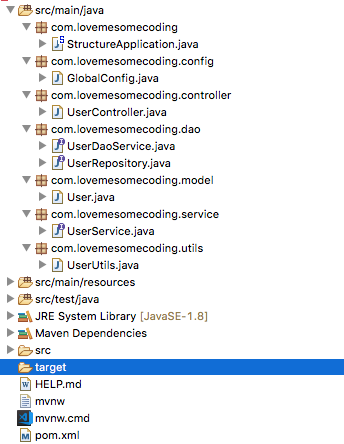
Entity Driven Layout
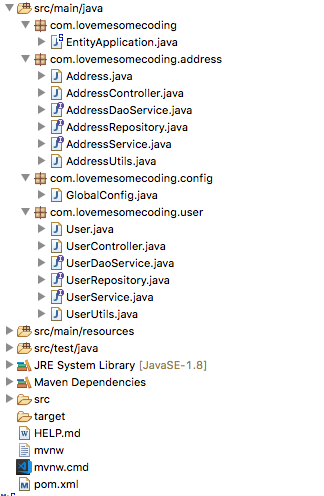
Layout and structure is a matter of preference. When you choose a layout in most cases you will have to stick to that layout and not change. You can mix and match but I don’t recommend this approach as it would make the project very hard to follow.
I usually go with the entity driven layout because it is easier for me to follow my project that way. I can find what I am looking for 99% of the time just by looking at the packages without having to drill down to the classes. Not only that I can really use encapusulation to make that services only access other services on the service layer not on the DAO layer.
June 3, 2019