Spring Security – Authentication
First you need to the spring-boot-starter-security in you pox.xml
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency>
Configure Spring security using java. This configuration is for APIs.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider;
@Autowired
private CustomLogoutHandler customLogoutHandler;
@Autowired
private CustomLogoutSuccessHandler customLogoutSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private CustomAcccessDeniedHandler customAcccessDeniedHandler;
@Bean
public CustomLoginFilter customUsernamePassworAuthenticationFilter() throws Exception {
return new CustomLoginFilter(PathConstantUtil.LOGIN_URL,authenticationManagerBean());
}
@Bean
public CustomAuthenticationFilter customAuthenticationFilter() {
return new CustomAuthenticationFilter();
}
@Bean
public RegistrationBean jwtAuthFilterRegister(CustomAuthenticationFilter customAuthenticationFilter) {
FilterRegistrationBean<CustomAuthenticationFilter> registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<CustomAuthenticationFilter>(
customAuthenticationFilter);
registrationBean.setEnabled(false);
return registrationBean;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// rest call rules
http
.cors().and().csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.PING_URL).permitAll()
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.LOGIN_URL).permitAll()
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.SIGNUP_URL).permitAll()
.anyRequest().permitAll();
// logout
http.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher(PathConstantUtil.LOGOUT_URL))
.addLogoutHandler(customLogoutHandler)
.logoutSuccessHandler(customLogoutSuccessHandler);
// filter
http.addFilterBefore(customUsernamePassworAuthenticationFilter(),UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
http.addFilterBefore(customAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// stateless
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
// handler access denied calls
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(customAcccessDeniedHandler);
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder) throws Exception {
builder.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider);
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.SIGNUP_URL)
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.LOGIN_URL)
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.PING_URL)
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.AUTH_TOKEN_URL)
.antMatchers(PathConstantUtil.SWAGGER_DOC_URLS)
.antMatchers("/actuator/**");
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
return encoder;
}
@Bean
public MethodInvokingFactoryBean methodInvokingFactoryBean() {
MethodInvokingFactoryBean methodInvokingFactoryBean = new MethodInvokingFactoryBean();
methodInvokingFactoryBean.setTargetClass(SecurityContextHolder.class);
methodInvokingFactoryBean.setTargetMethod("setStrategyName");
methodInvokingFactoryBean.setArguments(SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL);
return methodInvokingFactoryBean;
}
}
Here we configure our AuthenticationManager, PasswordEncoder, and web security for http routes.
Configure your Authentication Provider
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* Authenticate user by credentials
*
* @author fkaveinga
* @return Authentication
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("authenticate(...)");
String email = authentication.getPrincipal().toString();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
log.info("email: {}", email);
log.info("password: {}", password);
Map<String, String> details = (Map) authentication.getDetails();
log.debug("details: {}", ObjectUtils.toJson(details));
return loginWithPassword(email, password);
}
private Authentication loginWithPassword(String email, String password) {
log.info("loginWithPassword({})", email);
Optional<User> optUser = userService.findByEmail(email);
if (!optUser.isPresent()) {
log.info("user not found");
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Username or password is invalid");
}
log.info("user found for {}", email);
User user = optUser.get();
log.info("user: {}", ObjectUtils.toJson(user));
if (user.getPassword() == null || !PasswordUtils.verify(password, user.getPassword())) {
log.info("login credentials not matched");
throw new BadCredentialsException("Username or password is invalid");
}
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getEmail(), user.getPassword(), generateAuthorities(user.getRoles()));
}
/**
* Get Authorities for User
*
* @param user
* @return List<GrantedAuthority>
*/
private List<GrantedAuthority> generateAuthorities(Set<Role> roles) {
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
if (roles.isEmpty()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("No role");
} else {
for (Role role : roles) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + role.getAuthority().toUpperCase()));
}
}
return authorities;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return authentication.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
Configure your Login Filter to handle login
public class CustomLoginFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private Map<String,String> authenticationDetails = new HashMap<>();
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public CustomLoginFilter(String loginUrl, AuthenticationManager authManager) {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher(loginUrl));
setAuthenticationManager(authManager);
}
/**
* Attemp Authentication process. Pass username and password to authentication provider
* @author fkaveinga
* @return Authentication
*/
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
String authorizationHeader = request.getHeader("authorization");
log.info("Login Authorization Header: {}",authorizationHeader);
if(authorizationHeader==null) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("Authorization Header is null");
}
String email = getUsername(authorizationHeader);
String password = getPassword(authorizationHeader);
log.debug("email: {}",email);
log.debug("password: {}",password);
if(email == null || email.isEmpty()) {
log.info("username is null");
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("Username is null");
}
if(password == null || password.isEmpty()) {
log.info("password is null");
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("Password is null");
}
authenticationDetails.put("test", "good");
return authenticateWithPassword(email, password);
}
private Authentication authenticateWithPassword(String email, String password) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(email, password);
usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.setDetails(authenticationDetails);
return getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken);
}
/**
* Write response when request was successful.
* @author fkaveinga
* @return HttpServletResponse
*/
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.debug("successfulAuthentication(...)");
String clientIpAddress = HttpUtils.getRequestIP(request);
String clientUserAgent = HttpUtils.getRequestUserAgent(request);
String email = authResult.getPrincipal().toString();
User user = this.userService.getByEmail(email);
JwtPayload jwtpayload = new JwtPayload(user, RandomGeneratorUtils.getUuid());
jwtpayload.setDeviceId(clientUserAgent);
String jwtToken = JwtTokenUtils.generateToken(jwtpayload);
SessionDTO sessionDto = new SessionDTO();
sessionDto.setEmail(email);
sessionDto.setName(user.getName());
sessionDto.setUserUid(user.getUid());
sessionDto.setToken(jwtToken);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value());
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
ObjectUtils.getObjectMapper().writeValue(response.getWriter(),sessionDto);
}
/**
* Write response when request was unsuccessful.
* @author fkaveinga
* @return HttpServletResponse
*/
@Override
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.debug("unsuccessfulAuthentication(...)");
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
String message = failed.getLocalizedMessage();
log.debug("Error message: {}",message);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
ObjectNode result = ObjectUtils.getObjectNode();
result.put("status", "invalid email or password");
ObjectUtils.getObjectMapper().writeValue(response.getWriter(), result);
}
/**
* Parse token for username
* @param authorizationHeader
* @return String username
*/
private String getUsername(String authorizationHeader) {
log.debug("getUsername(..)");
String username = null;
try {
String usernamePasswordToken = StringUtils.substringAfter(authorizationHeader, " ").trim();
//log.info("usernamePasswordToken: {}",usernamePasswordToken);
String rawToken = this.decodeBase64Token(usernamePasswordToken);
log.debug("rawToken: {}",rawToken);
username = StringUtils.substringBefore(rawToken, ":");
log.debug("username: {}",username);
return username;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return username;
}
/**
* Parse token for password
* @param authorizationHeader
* @return String password
*/
private String getPassword(String authorizationHeader) {
log.debug("getPassword(..)");
String password = null;
try {
String usernamePasswordToken = StringUtils.substringAfter(authorizationHeader, " ").trim();
String rawToken = this.decodeBase64Token(usernamePasswordToken);
log.debug("rawToken: {}",rawToken);
password = StringUtils.substringAfter(rawToken, ":");
log.debug("username: {}",password);
return password;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return password;
}
/**
* Parse for access token
* @param authorizationHeader
* @return String access token
*/
private String getAccessToken(String authorizationHeader) {
log.debug("getAccessToken(..)");
String bearerToken = null;
try {
bearerToken = StringUtils.substringAfter(authorizationHeader, " ").trim();
log.info("bearerToken: {}",bearerToken);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bearerToken;
}
/**
* Decode authentication token
* @param usernamePasswordToken
* @return String
*/
private String decodeBase64Token(String usernamePasswordToken) {
byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(usernamePasswordToken);
return new String(decodedBytes);
}
}
May 30, 2019 Git stash
The git stash command is used to stash away your current work and revert back to a clean working directory which matches the HEAD commit.
Let’s say for example that you are in a middle of working on a feature branch and suddenly a customer issue comes up. At this point you want to commit your code but cannot and you want to save it. This is when git stash comes in handy. You can stash your changes and come back to them later after you fix the customer issue.
Note that git stash is stored locally and is not pushed to your git server.
How to stash
Stash your current changes
git stash
Stash your current changes with a message to help you remember
git stash save "message"
You can stash multiple changes in which case they will be in a list.
How to see your stashes
List your stashes
git stash list
See stash summary
git stash show
See stash full diff
git stash show -p
How to apply back your stash(es)
Apply the first stash to your code and remove that first stash from the list
git stash pop
Apply the second stash to your code and remove that second stash from the list
git stash pop stash@{1}
if you want to apply the stash to your code but not remove it from your stash list then use:
git stash apply
How to remove a stash without applying it
Drop the second stash on the list
git stash drop stash@{1}
Remove all your stashes
git stash clear
How to stash partial work
This will iterate through your changes and ask you which file to stash
git stash -p
Spring boot – bean
Spring beans are Java POJO classes created, wired, configured, and managed by the Spring container from start to finish. The Spring container uses DI to manage the components that make up an application.
The Spring container gets its instructions on what objects to instantiate, configure, and assemble by reading the configuration metadata(Configuration classes) provided. The configuration metadata can be represented either by XML, Java annotations, or Java code. The Spring IoC container makes use of Java POJO classes and configuration metadata to produce a fully configured and executable system or application.
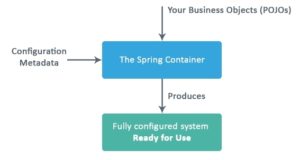
Add Java configuration class
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.lovemesomecoding.service.UserService;
import com.lovemesomecoding.service.UserServiceImpl;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public UserService userService() {
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
return userService;
}
}
Spring Boot Rest
May 22, 2019MySQL Functions
LAST_INSERT_ID Function
The LAST_INSERT_ID functions returns the last id of the column that uses AUTO_INCREMENT for its id. It’s also important to know that this function has be called after an insert or else if you just call it without an insert statement it will give you 0.
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
REPLACE Function
REPLACE function replaces a substring within a string with another string. This is very helpful when updating rows.
REPLACE(str,lookingFor,replacement);
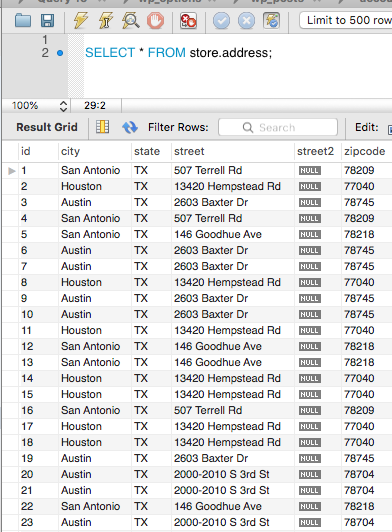
Now we are updating rd to Road in street address
CONCAT Function
The CONCAT function concatenates two or more strings together to a single string. It can be used in SELECT statements to concatenate column values.
SELECT CONCAT(column1,column2, ... ) as alias FROM table_name;
Here is an example of the CONCAT function.
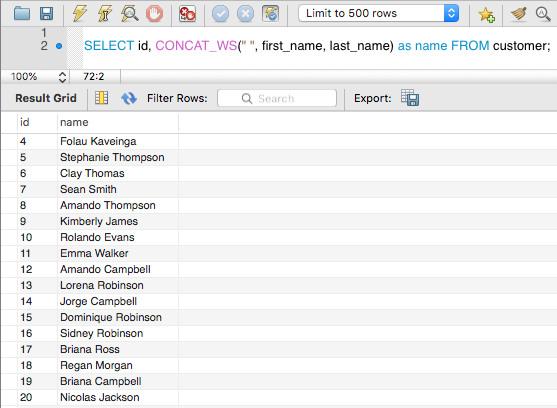
CONCAT_WS Function
The CONCAT_WS concatenates strings or columns together with a separator.
Here is an example of the CONCAT_WS function with a ” ” separator.
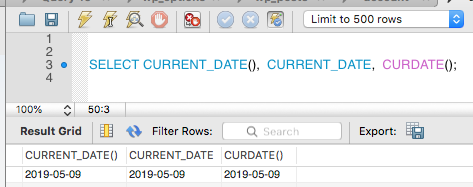
CURDATE Function (CURRENT_DATE or CURRENT_DATE() are same to CURDATE)
The CURDATE function returns the current date in the format of ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ for string format.
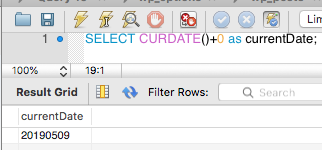
For numeric format, add +0 like the example below.
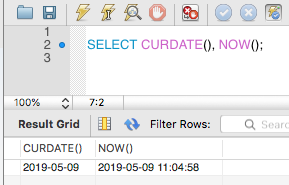
The CURDATE function is different from the NOW function. The NOW function returns both date and time of the current time.
DATEDIFF Function
The DATEDIFF function calculates the number of days between two DATE, DATETIME, or TIMESTAMP values. If you pass in a DATETIME or TIMESTAMP, the DATEDIFF function only takes the date part and ignores the time part.
SELECT DATEDIFF(date_expression_1,date_expression_2) FROM table_name;
TIMEDIFF Funciton
The TIMEDIFF calculates the time difference between two TIME or DATETIME values. Note here that these two values must be of the same data type. They must be either both TIME or both DATETIME. It one is TIME and the other is DATETIME, MySQL will return a NULL.
SELECT TIMEDIFF(time_expression_1,time_expression_2) FROM table_name;
The result of TIMEDIFF is of this range -838:59:59 to 838:59:59which is about 35 days worth of time.
Here is an example of TIMEDIFF with TIMEs
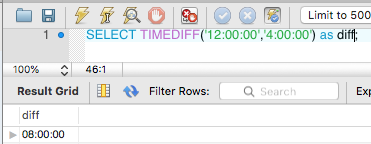
Here is an example of TIMEDIFF with DATETIMEs
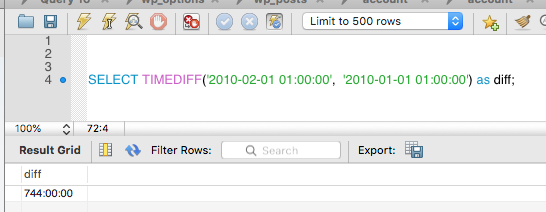
TIMESTAMPDIFF Function
The TIMESTAMPDIFF function calculates the difference between two DATE or DATETIME values. The calculation is begin_timestamp – end_timestamp. These two values can be of mix data type DATE or DATETIME.
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit,begin_timestamp,end_timestamp) FROM table_name;
Unit can be: MICROSECOND, SECOND, MINUTE, HOUR, DAY, WEEK, MONTH, QUARTER, YEAR
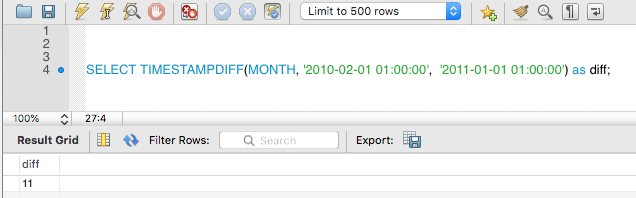
Here is an example of mix formats
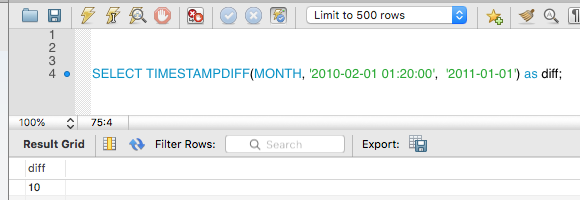
A practical example is finding user’s age.
SELECT id, TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR, date_of_birth, NOW()) age FROM users;
DATETIME vs TIMESTAMP
TIMESTAMP has a timezone but DATETIME does not.
May 8, 2019