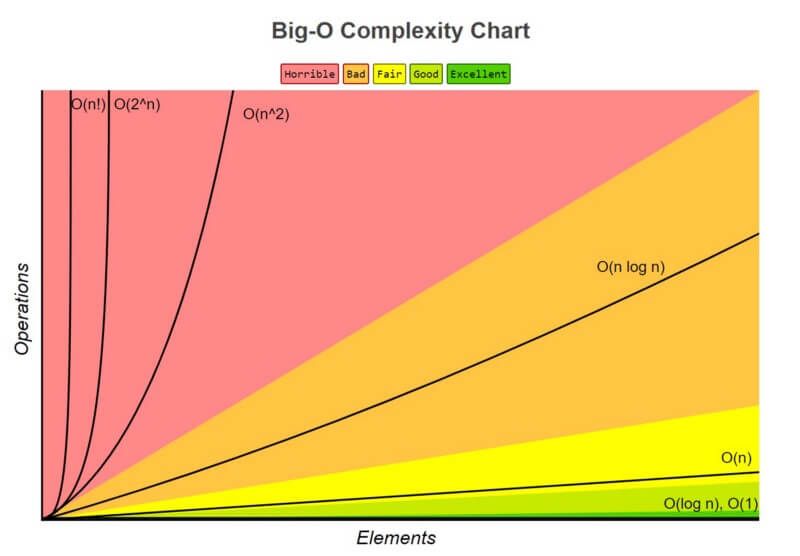
Big O Notation
Big O is about how long an algorithm takes to run from start to end and how well it scales as the size of the input or dataset increases.
Big O is mostly measured based on the worst-case scenario even though some algorithms might finish earlier than others.
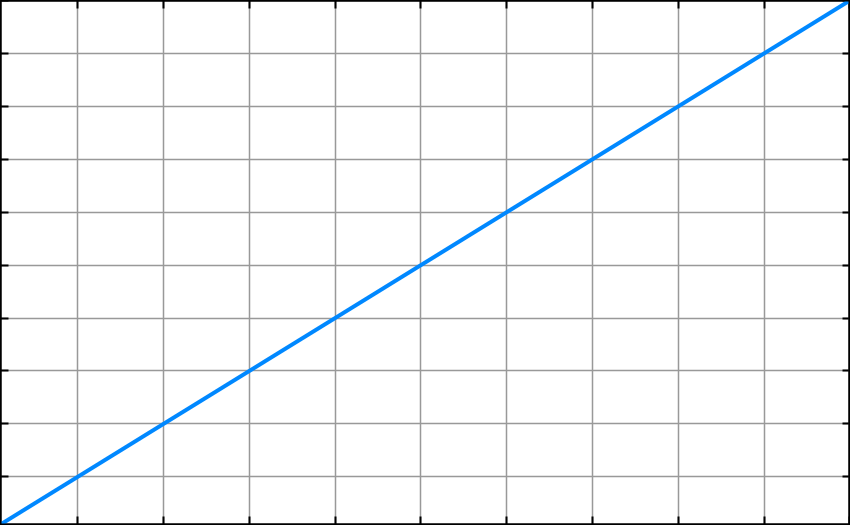
Here is another graph for more clarity.

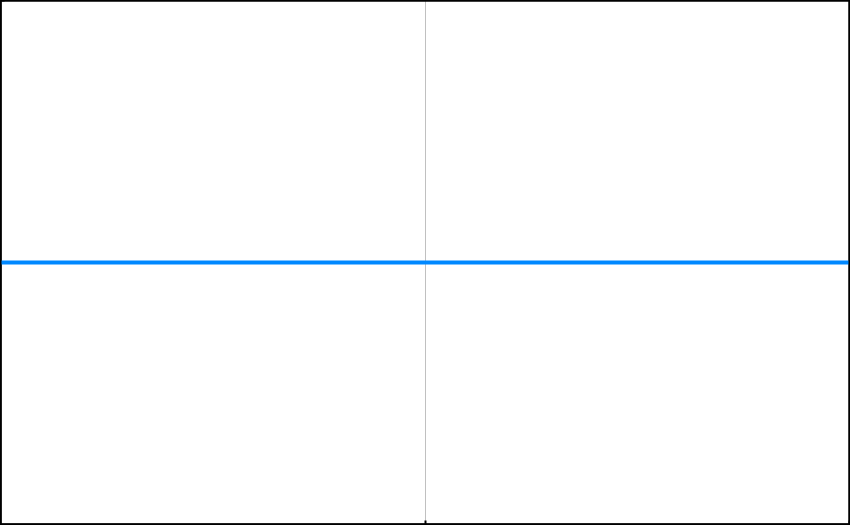
O(1) – constant time This runtime is said to be fixed or constant. It does not matter how big the input or dataset is, the algorithm takes the same amount of time to run. This means that the size of the dataset is irrelevant, the algorithm will always take a constant time. 1 item takes 1 second, 10 items take 1 second, 100 items take 1 second. It always takes the same amount of time.
public int getFirstItem(int[] items) {
return items[0];
}
This function above takes an int array (items). But regardless of the size of the input array, it will always take one step to run(return the first item)

O(n) – n time or linear time
public void sendWelcomeNoteToUsers(User[] users) {
for (User user : users) {
emailService.sendNote(user);
...
}
}
As the size of the array of users increases, the sendWelcomeNoteToUsers method runtime increases. Dataset and time taken grow proportionately. 1 item takes 1 second, 10 items take 10 seconds, 100 items take 100 seconds. Sometimes you might see something like this and think differently.
public User getUserByEmail(User[] users, String email){
for (int i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {
if (users[i].equals(email)) {
return users[i];
}
}
}
Even though the getUserByEmail method might find a user early and not get to the end of the array. Big O is based on the worst-case scenario of an algorithm so it is still O(n).
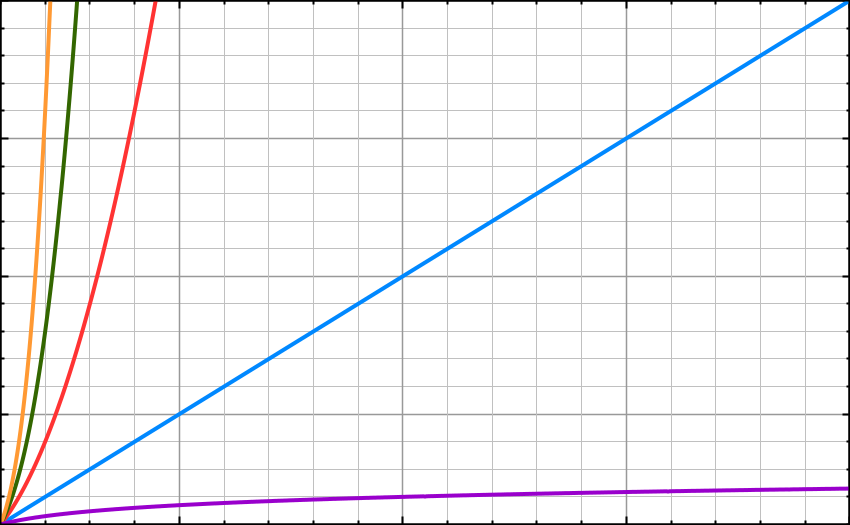
O(N²) – n square or quadratic time The Quadratic time or n square time increases at twice the rate of O(n).
public static void suspendAllUsersWithinPlans(Plan[] plans) {
for (Plan plan : plans) {
List<User> users = plan.getUsers();
for (User user : users) {
// suspend logic goes here.
}
}
}
This runtime is extra slow. 1 item takes 1 second, 10 items take 100, 100 items take 10000. The outer loop runs n times and the inner loop runs n times for each iteration of the outer loop, giving us n². Bubble sort is an example of quadratic time complexity.
private static void bubble_sort(int[] input, boolean ascending) {
int inputLength = input.length;
int temp;
boolean is_sorted;
for (int i = 0; i < inputLength; i++) {
is_sorted = true;
for (int j = 1; j < (inputLength - i); j++) {
if (ascending) {
if (input[j - 1] > input[j]) {
temp = input[j - 1];
input[j - 1] = input[j];
input[j] = temp;
is_sorted = false;
}
} else {
if (input[j - 1] < input[j]) {
temp = input[j - 1];
input[j - 1] = input[j];
input[j] = temp;
is_sorted = false;
}
}
}
// is sorted? then break it, avoid useless loop.
if (is_sorted) break;
}
}
As you can see, bubble sort has two for loops. An outer loop and an inner loop.

O(log n) – log n time The log n time is the opposite of n². Logarithm is the opposite of exponential. Exponential grows by being multiplied and logarithm grows(gettings smaller) by being divided. Log n is the case when a set of data is repeatedly divided into half and the middle element is processed. This means that for one iteration of the algorithm, technically speaking, two items are processed. O(log n) is not as good as constant, but still pretty good. Log n increases with the size of the data set, but not proportionately. This means the algorithm takes longer per item on smaller datasets relative to larger ones. 1 item takes 1 second, 10 items take 2 seconds, 100 items take 3 seconds. If your dataset has 10 items, each item causes 0.2 seconds latency. If your dataset has 100, it only takes 0.03 seconds extra per item. This makes log n algorithms very scalable. Binary Search(sorted dataset) is the primary example of the log n.
public static int binarySearch(int[] elements, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = elements.length - 1;
while (left <= right)
{
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (target < elements[middle])
{
right = middle - 1;
}
else if (target > elements[middle])
{
left = middle + 1;
}
else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr1 = {-20, 3, 15, 81, 432};
// test when the target is in the middle
int index = binarySearch(arr1,15);
System.out.println(index);
// test when the target is the first item in the array
index = binarySearch(arr1,-20);
System.out.println(index);
// test when the target is in the array - last
index = binarySearch(arr1,432);
System.out.println(index);
// test when the target is not in the array
index = binarySearch(arr1,53);
System.out.println(index);
}

O(n log n) – n log n This runtime is the case when a set of data is repeatedly divided into half and each half is processed again independently.
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < 8; j = j * 2) {
System.out.println("Hey - I'm busy looking at: " + i + " and " + j);
}
}

O(2^n) – exponential growth This runtime grows exponentially. Adding one element to the input dramatically increases the processing time. For example. Let’s say you are to find combinations; if you have a list of 150 people and you would like to find every combination of groupings; everyone by themselves, all of the groups of 2 people, all of the groups of 3 people, etc. Using a simple program which takes each person and loops through the combinations, if I add one extra person then it’s going to increase the processing time exponentially. Every new element will double the processing time. O(kn) algorithms will get k times bigger with every additional input. O(2n) algorithms double it’s processing time with every additional input. O(3n) algorithms triple it’s processing time with every additional input.
int k = 5;
int n = 6;
int power = (int)Math.pow(k, n);
System.out.println("power: " + power);
for (int i = 1; i <= power; i++){
System.out.println("Hey - I'm busy looking at: " + i);
}
O(n!) – factorial time In most cases, this is the worst runtime. This class of algorithms has a run time proportional to the factorial of the input size.
for (int i = 1; i <= factorial(n); i++) {
System.out.println("Hey - I'm busy looking at: " + i);
}
....
public int factorial(int number) {
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
fact = fact * i;
}
return fact;
}


Space Complexity Space complexity is the space used by the input values plus auxiliary space which is the extra space or the temporary space used by the algorithm during its execution. Space complexity = auxiliary space + input space
public static int getLargestItem(int[] items) {
int largest = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int item : items) {
if (item > largest) {
largest = item;
}
}
return largest;
}
The variable largest takes some space to hold the int min value. Similar to Time Complexity, Space complexity also plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency of an algorithm/program. If an algorithm takes up a lot of time, you can still wait, run/execute it to get the desired output. But, if a program takes up a lot of memory space, the compiler will not let you run it.