Heap
Heap is a tree-based data structure in which all the nodes of the tree are in a specific order. Heap is a complete binary tree-based data structure. Heaps have specific ordering properties. The ordering can be one of two types:
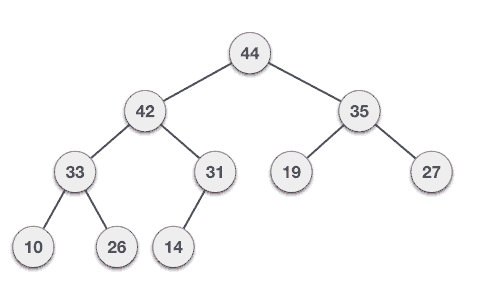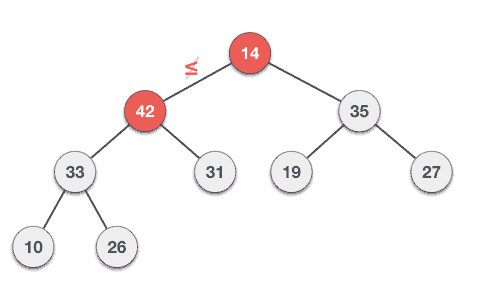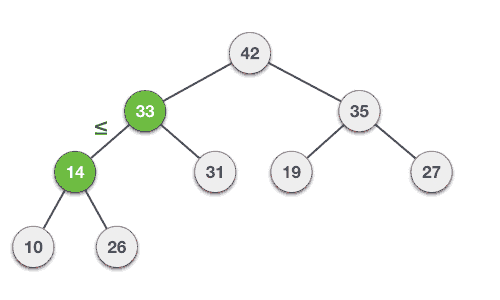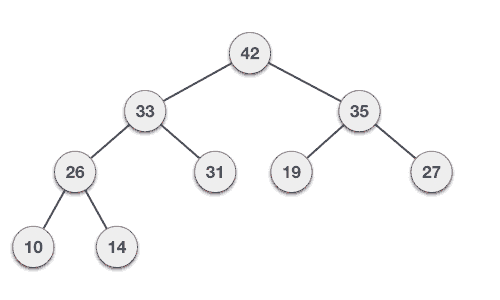
- Max-Heap: The value of a node must be greater than or equal to the values of its children. The greatest value is at the root. The same property must be true for all subtrees.
35 33 42 10 14 19 27 44 26 31
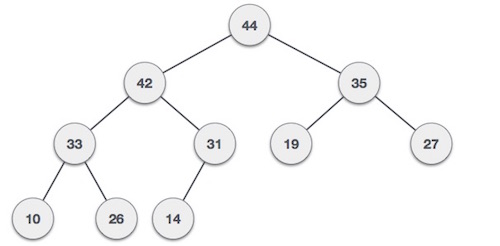
Max-Heap construction

Max-Heap deletion
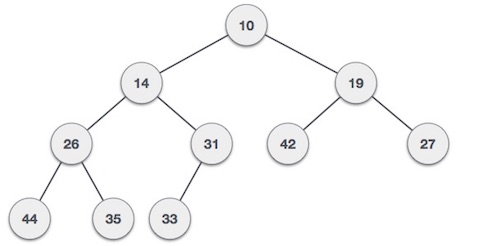
@NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Data @ToString public class MaxHeap { private List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<>(); /** * Function to return the position of the parent for the node currently at position */ private int parent(int position) { if (position == 0) { return 0; } return (position - 1) / 2; } /** * Function to return the position of the left child for the node currently at position */ private int left(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } /** * Function to return the position of the right child for the node currently at position */ private int right(int position) { return (2 * position) + 2; } private void swap(int firstPosition, int secondPosition) { System.out.println("firstPosition: " + firstPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(firstPosition) + ", secondPosition: " + secondPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(secondPosition)); int tmp = this.data.get(firstPosition); this.data.set(firstPosition, this.data.get(secondPosition)); this.data.set(secondPosition, tmp); System.out.println("firstPosition: " + firstPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(firstPosition) + ", secondPosition: " + secondPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(secondPosition)); } public void add(int item) { this.data.add(item); // increase the size of an array Heap[++size] = element; int current = getSize() - 1; System.out.println("adding: " + item + " to position: " + current); heapifyUp(current); } public int peek() { return data.get(0); } /** * Step 1 − Remove root node.<br> * Step 2 − Move the last element of last level to root.<br> * Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent.<br> * Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them.<br> * Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.<br> */ public int poll() { int head = data.get(0); // replace the root of the heap with the last element data.set(0, this.data.get(getSize() - 1)); data.remove(getSize() - 1); // call heapify-down on the root node heapifyDown(0); return head; } /** * Step 1 − Create a new node at the end of heap.<br> * Step 2 − Assign new value to the node.<br> * Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent.<br> * Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them.<br> * Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.<br> */ private void heapifyUp(int position) { int temp = this.data.get(position); if (position > 0 && temp > this.data.get(parent(position))) { System.out.println("heapifyUp - position: " + position + ", data: " + this.data.get(parent(position))); // swap the two if heap property is violated swap(position, parent(position)); // call heapify-up on the parent heapifyUp(parent(position)); } } /** * Step 1 − Remove root node.<br> * Step 2 − Move the last element of last level to root.<br> * Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent.<br> * Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them.<br> * Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.<br> */ private void heapifyDown(int position) { int largest = position; int leftChild = left(position); int rightChild = right(position); // compare `A[i]` with its left and right child // and find the largest value int size = getSize(); if (leftChild < size && this.data.get(leftChild) > this.data.get(largest)) { largest = leftChild; } if (rightChild < size && this.data.get(rightChild) > this.data.get(largest)) { largest = rightChild; } if (largest != position) { // swap with a child having lesser value swap(position, largest); // call heapify-down on the child heapifyDown(largest); } } public void print() { System.out.println("\nList"); for (Integer d : data) { System.out.println("data: " + d); } System.out.println("\nTree"); System.out.println("Root: " + data.get(0)); for (int i = 1; i <= getSize() / 2; i++) { try { System.out.print("Parent: " + this.data.get(i - 1)); } catch (Exception e) { } try { System.out.print(", Left: " + this.data.get(this.left(i - 1))); } catch (Exception e) { } try { System.out.print(", Right: " + this.data.get((this.right(i - 1)))); } catch (Exception e) { } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("\n"); } public int getSize() { return this.data.size(); } } - Min-Heap: The value of a node is greater than or equal to the value of its parent. The smallest value is at the root. The same property must be true for all subtrees.
35 33 42 10 14 19 27 44 26 31
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ToString
public class MinHeap {
private List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Function to return the position of the parent for the node currently at position
*/
private int parent(int position) {
if (position == 0) {
return 0;
}
return (position - 1) / 2;
}
/**
* Function to return the position of the left child for the node currently at position
*/
private int left(int position) {
return (2 * position) + 1;
}
/**
* Function to return the position of the right child for the node currently at position
*/
private int right(int position) {
return (2 * position) + 2;
}
private void swap(int firstPosition, int secondPosition) {
System.out.println("firstPosition: " + firstPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(firstPosition) + ", secondPosition: " + secondPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(secondPosition));
int tmp = this.data.get(firstPosition);
this.data.set(firstPosition, this.data.get(secondPosition));
this.data.set(secondPosition, tmp);
System.out.println("firstPosition: " + firstPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(firstPosition) + ", secondPosition: " + secondPosition + ", data: " + this.data.get(secondPosition));
}
public void add(int item) {
this.data.add(item);
// increase the size of an array Heap[++size] = element;
int current = getSize() - 1;
System.out.println("adding: " + item + " to position: " + current);
heapifyUp(current);
}
public int peek() {
return data.get(0);
}
public int poll() {
int head = data.get(0);
// replace the root of the heap with the last element
data.set(0, this.data.get(getSize() - 1));
data.remove(getSize() - 1);
// call heapify-down on the root node
heapifyDown(0);
return head;
}
/**
* Step 1 − Create a new node at the end of heap.<br>
* Step 2 − Assign new value to the node.<br>
* Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent.<br>
* Step 4 − If value of parent is greater than child, then swap them.<br>
* Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.<br>
*/
private void heapifyUp(int position) {
int temp = this.data.get(position);
if (position > 0 && temp < this.data.get(parent(position))) {
System.out.println("heapifyUp - position: " + position + ", data: " + this.data.get(parent(position)));
// swap the two if heap property is violated
swap(position, parent(position));
// call heapify-up on the parent
heapifyUp(parent(position));
}
}
/**
* Step 1 − Remove root node.<br>
* Step 2 − Move the last element of last level to root.<br>
* Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent.<br>
* Step 4 − If value of parent is greater than child, then swap them.<br>
* Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.<br>
*/
private void heapifyDown(int position) {
int smallest = position;
int leftChild = left(position);
int rightChild = right(position);
// compare `A[i]` with its left and right child
// and find the smallest value
int size = getSize();
if (leftChild < size && this.data.get(leftChild) < this.data.get(smallest)) {
smallest = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < size && this.data.get(rightChild) < this.data.get(smallest)) {
smallest = rightChild;
}
if (smallest != position) {
// swap with a child having lesser value
swap(position, smallest);
// call heapify-down on the child
heapifyDown(smallest);
}
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("\nList");
for (Integer d : data) {
System.out.println("data: " + d);
}
System.out.println("\nTree");
System.out.println("Root: " + data.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i <= getSize() / 2; i++) {
try {
System.out.print("Parent: " + this.data.get(i - 1));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
System.out.print(", Left: " + this.data.get(this.left(i - 1)));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
System.out.print(", Right: " + this.data.get((this.right(i - 1))));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
public int getSize() {
return this.data.size();
}
}
Heap Data Structure Applications
- Heap is used while implementing a priority queue.
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- Heap Sort