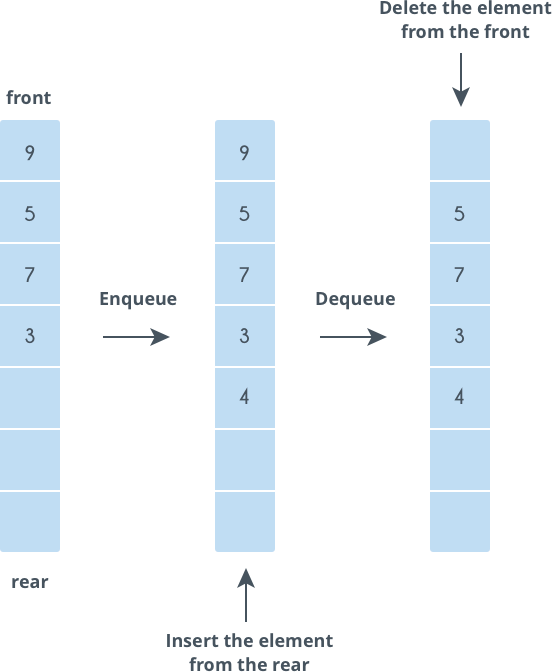
Queue
Queue is an ordered list in which insertions are done at one end (back) and deletions are done at other end (front). The first element to be inserted is the first one to be deleted. Hence, it is called First in First out (FIFO) or Last in Last out (LILO) list.
In general, a queue is a line of people or things waiting to be served in sequential order starting at the beginning of the line or sequence.
When an element is inserted in a queue, the concept is called EnQueue, and when an element is removed from the queue, the concept is called DeQueue. DeQueueing an empty queue is called underflow and EnQueuing an element in a full queue is called overflow.
Basic features of Queue
- Like stack, queue is also an ordered list of elements of similar data types.
- Queue is a FIFO( First in First Out ) structure.
- Once a new element is inserted into the Queue, all the elements inserted before the new element in the queue must be removed, to remove the new element.
peek()function is oftenly used to return the value of first element without dequeuing it.
Applications of Queue
Queue, as the name suggests is used whenever we need to manage any group of objects in an order in which the first one coming in, also gets out first while the others wait for their turn, like in the following scenarios:
-
- Serving requests on a single shared resource, like a printer, CPU task scheduling etc.
- Operating systems schedule jobs (with equal priority) in the order of arrival (e.g., a print queue).
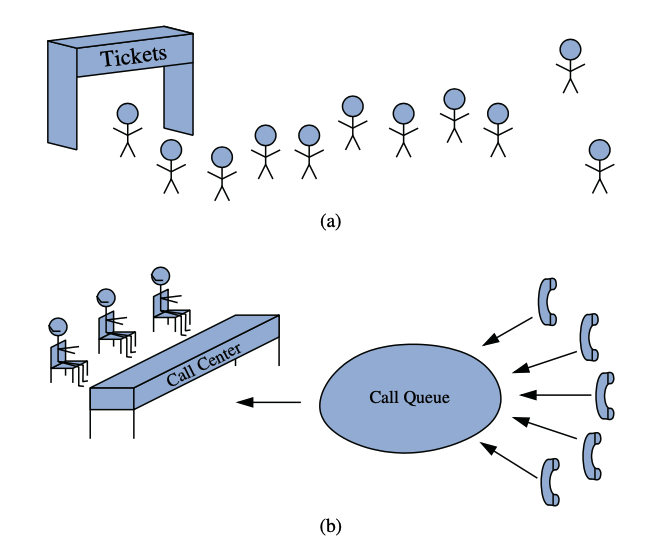
- Simulation of real-world queues such as lines at a ticket counter, or any other first- come first-served scenario requires a queue.
- In real life scenario, Call Center phone systems uses Queues to hold people calling them in an order, until a service representative is free.
- Handling of interrupts in real-time systems. The interrupts are handled in the same order as they arrive i.e First come first served.
- Asynchronous data transfer (file IO, pipes, sockets).
- Determining number of cashiers to have at a supermarket.
Time Complexity of Queue Operations
Just like Stack, in case of a Queue too, we know exactly, on which position new element will be added and from where an element will be removed, hence both these operations requires a single step.
- Enqueue: O(1)
- Dequeue: O(1)
- Size: O(1)
Implementations of Queue
Queue can be implemented using an Array, List, or Linked List. LinkedList has the best performance.
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class MyQueue<E> {
private LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<>();
public E enqueue(E item) {
list.addFirst(item);
return item;
}
public E dequeue() {
if (list.size() <= 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return list.removeLast();
}
public int getSize() {
return list.size();
}
public void print() {
int size = getSize();
int count = 1;
if (count >= size) {
return;
}
E item = list.getFirst();
while (item != null) {
System.out.println(item.toString());
if (count >= size) {
break;
}
item = list.get(count);
count++;
}
}
}